The efficacy and safety of Xueshuantong (lyophilized) for injection in the treatment of unstable angina pectoris: A systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 37089918
- PMCID: PMC10119405
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1074400
The efficacy and safety of Xueshuantong (lyophilized) for injection in the treatment of unstable angina pectoris: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
Objective: Xueshuantong (lyophilized) for injection (XST) is an effective botanical drug for treating unstable angina pectoris (UAP). However, a meta-analysis of XST combined with conventional treatment (CT) against UAP has not been conducted. Therefore, this study aimed to investigate the effectiveness and safety of XST combined with CT for UAP patients compared to CT alone. Methods: Randomized controlled trials (RCT) of XST in UAP patients were retrieved from the Cochrane Library, PubMed, Web of Science, EMBASE, CNKI, VIP, Wanfang, and Chinese Biological Medicine Database databases. A meta-analysis was performed using Revman 5.4 and Stata 16.0, and the quality of the included literature was evaluated based on the Cochrane risk-of-bias 2.0 (RoB2.0) tool. The aggregate 95% confidence intervals (CIs), mean difference (MD), and relative risk (RR) estimates were calculated. A GRADE assessment was performed using GRADEprofiler 3.6, and trial sequent analysis was performed using TSA 0.9. Results: Thirty-four studies involving 3,518 patients were included in the analysis. The combination of CT with XST improved the comprehensive clinical efficacy (RR = 1.22, 95% CI: 1.18-1.26, p < 0.00001) and ECG improvement (RR = 1.24, 95% CI: 1.18-1.31, p < 0.00001). The frequency of angina attacks was lower (MD = -0.73, 95% CI: -0.92 to -0.55, p < 0.00001), and the duration was shorter (MD = -1.08, 95% CI: -1.44 to -0.72, p < 0.00001) in the group that received CT combined with XST compared to the one without XST. Total cholesterol levels (MD = -1.30, 95% CI: -1.83 to -0.78, p < 0.00001) and triglyceride levels (MD = -0.76, 95% CI: -0.93 to -0.59, p < 0.00001) were lower in patients who received CT in combination with XST than those who received CT alone. CT combined with XST reduced whole blood viscosity (MD = -0.72, 95% CI = -0.99 to -0.44, p < 0.00001) and plasma viscosity (MD = -0.24, 95% CI: -0.46 to -0.03, p = 0.03). There was no statistically significant difference in the incidence of cardiovascular events or adverse events among patients treated with the combination of XST and CT compared to CT alone. The GRADE assessment indicated that the composite quality of the evidence was low. The trial sequent analysis showed an adequate sample size and stable findings for the clinical efficacy of CT combined with XST for unstable angina. Conclusion: The present systematic review and meta-analysis conditionally indicate that XST combined with CT improved the clinical outcomes of patients with unstable angina more than CT alone with a better safety profile. However, the results need further validation due to limitations in the quality of the included studies. Systematic Review Registration: https://www.crd.york.ac.uk/PROSPERO/, identifier CRD42022357395.
Keywords: GRADE; Xueshuantong for injection; meta-analysis; trial sequential analysis; unstable angina pectoris.
Copyright © 2023 Xi, Wei, Cui, Liu and Xie.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
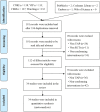
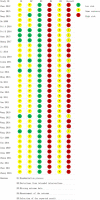
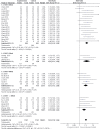
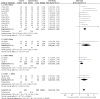

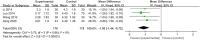
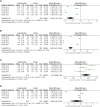
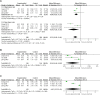

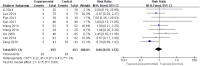

References
-
- Chen J. H., Wang J. L. (2019). Effect of ginseng and Taohong Siwu decoction on cardiac function and blood lipids in patients with angina pectoris of coronary heart disease. China Med. Her. 16 (24), 135–138.
-
- Chen T. N., Ge C. J., Yang J., Sun G. (2012). Clinical observation of Xueshuantong injection in the treatment of unstable angina pectoris. Mod. Med. Health 28 (19), 2909–2910.
-
- Chen Z. (2015). Clinical analysis of Xueshuantong in the treatment of coronary heart disease and angina pectoris in the elderly. World's latest Med. Inf. Abstr. 15 (55), 94.
-
- Chinese Medical Association Cardiology Branch, editorial Board of Chinese Journal of Cardiovascular Diseases (2007). Guidelines for diagnosis and treatment of unstable angina pectoris and non-St segment elevation myocardial infarction. Chin. J. Cardiovasc. Dis. 35(4), 295–304.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

