Evaluation of mulberry leaves' hypoglycemic properties and hypoglycemic mechanisms
- PMID: 37089923
- PMCID: PMC10117911
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1045309
Evaluation of mulberry leaves' hypoglycemic properties and hypoglycemic mechanisms
Abstract
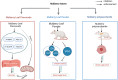
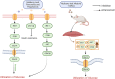
The effectiveness of herbal medicine in treating diabetes has grown in recent years, but the precise mechanism by which it does so is still unclear to both medical professionals and diabetics. In traditional Chinese medicine, mulberry leaf is used to treat inflammation, colds, and antiviral illnesses. Mulberry leaves are one of the herbs with many medicinal applications, and as mulberry leaf study grows, there is mounting evidence that these leaves also have potent anti-diabetic properties. The direct role of mulberry leaf as a natural remedy in the treatment of diabetes has been proven in several studies and clinical trials. However, because mulberry leaf is a more potent remedy for diabetes, a deeper understanding of how it works is required. The bioactive compounds flavonoids, alkaloids, polysaccharides, polyphenols, volatile oils, sterols, amino acids, and a variety of inorganic trace elements and vitamins, among others, have been found to be abundant in mulberry leaves. Among these compounds, flavonoids, alkaloids, polysaccharides, and polyphenols have a stronger link to diabetes. Of course, trace minerals and vitamins also contribute to blood sugar regulation. Inhibiting alpha glucosidase activity in the intestine, regulating lipid metabolism in the body, protecting pancreatic -cells, lowering insulin resistance, accelerating glucose uptake by target tissues, and improving oxidative stress levels in the body are some of the main therapeutic properties mentioned above. These mechanisms can effectively regulate blood glucose levels. The therapeutic effects of the bioactive compounds found in mulberry leaves on diabetes mellitus and their associated molecular mechanisms are the main topics of this paper's overview of the state of the art in mulberry leaf research for the treatment of diabetes mellitus.
Keywords: chemical substances in mulberry leaves; diabetes treatmen; molecular mechanism; mulberry leaves; mulberry leaves safety.
Copyright © 2023 Chen, Xi, Gao, Li, Dong, Geng, Liu, Huang, Wang, Li, Wei and Miao.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Mulberry leaves ameliorate diabetes via regulating metabolic profiling and AGEs/RAGE and p38 MAPK/NF-κB pathway.J Ethnopharmacol. 2022 Jan 30;283:114713. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2021.114713. Epub 2021 Oct 6. J Ethnopharmacol. 2022. PMID: 34626776
-
Isolation and hypoglycemic effects of water extracts from mulberry leaves in Northeast China.Food Funct. 2020 Apr 30;11(4):3112-3125. doi: 10.1039/d0fo00012d. Food Funct. 2020. PMID: 32196541
-
Novel active compounds and the anti-diabetic mechanism of mulberry leaves.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Oct 5;13:986931. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.986931. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 36278175 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical potential and mechanistic insights of mulberry (Morus alba L.) leaves in managing type 2 diabetes mellitus: Focusing on gut microbiota, inflammation, and metabolism.J Ethnopharmacol. 2023 Apr 24;306:116143. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2023.116143. Epub 2023 Jan 9. J Ethnopharmacol. 2023. PMID: 36632855 Review.
-
Effects and Mechanistic Role of Mulberry Leaves in Treating Diabetes and its Complications.Am J Chin Med. 2023;51(7):1711-1749. doi: 10.1142/S0192415X23500775. Epub 2023 Aug 30. Am J Chin Med. 2023. PMID: 37646143 Review.
Cited by
-
Allantoin reduces glucotoxicity and lipotoxicity in a type 2 diabetes rat model by modulating the PI3K and MAPK signaling pathways.Heliyon. 2024 Jul 18;10(15):e34716. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e34716. eCollection 2024 Aug 15. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 39144993 Free PMC article.
-
Insights into the Activities and Usefulness of Deoxynojirimycin and Morus alba: A Comprehensive Review.Molecules. 2025 Jul 31;30(15):3213. doi: 10.3390/molecules30153213. Molecules. 2025. PMID: 40807388 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Basic Study of the Effects of Mulberry Leaf Administration to Healthy C57BL/6 Mice on Gut Microbiota and Metabolites.Metabolites. 2023 Sep 10;13(9):1003. doi: 10.3390/metabo13091003. Metabolites. 2023. PMID: 37755283 Free PMC article.
-
Altering the bacterial community: sour soup decreased CO2 production and improved the fermentation quality of Broussonetia papyrifera, Tritriale and mixed silages.Front Microbiol. 2025 Jun 25;16:1606628. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2025.1606628. eCollection 2025. Front Microbiol. 2025. PMID: 40636507 Free PMC article.
-
Widely Targeted Metabolomics Analysis to Reveal Metabolite of Morus alba L. in Different Medicinal Parts.Molecules. 2024 Aug 23;29(17):3981. doi: 10.3390/molecules29173981. Molecules. 2024. PMID: 39274829 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources