Sijunzi decoction granules in the prevention and treatment of recurrence of colorectal adenoma: Study protocol for a multicenter, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial
- PMID: 37089947
- PMCID: PMC10113428
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1175811
Sijunzi decoction granules in the prevention and treatment of recurrence of colorectal adenoma: Study protocol for a multicenter, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial
Abstract
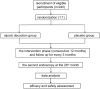
Background: The recurrence of colorectal adenomas (CRAs) after endoscopy predisposes patients to a risk of colorectal cancer. Guided by the traditional Chinese medicine (TCM), patients with colorectal diseases usually manifest with spleen deficiency syndrome (SDS) and are treated with Sijunzi decoction (SJZD). Therefore, this trial aims to explore the efficacy and safety of SJZD in the prevention and treatment of CRAs recurrence. Methods: SJZD on prevention and treatment of CRAs recurrence after resection: a multicenter, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial was designed. Patients who undergo polypectomy of CRAs will be recruited and randomized into a SJZD group and a placebo group in a 1:1 ratio. The intervention phase will be 12 months. The follow-up period will last 24 months. The primary outcome is the CRA recurrence rate after intervention. The secondary outcomes include the CRA recurrence rate at the second year post-polypectomy, the pathological type of adenoma and the alterations in SDS scores after intervention. Discussion: Previous clinical practice has observed the sound effect of SJZD in the context of gastrointestinal diseases. A number of experiments have also validated the active components in SJZD. This trial aims to provide tangible evidence for the usage of SJZD, hoping to reduce the recurrence of CRAs.
Keywords: Sijunzi decoction; colorectal adenoma; randomized controlled trial; spleen deficiency syndrome; traditional Chinese medicine.
Copyright © 2023 Ni, Liu, Liu, Lu, Zhou, Dai, Zhao, Xu and Ji.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources