Artificial intelligence and deep learning: New tools for histopathological diagnosis of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease/nonalcoholic steatohepatitis
- PMID: 37090431
- PMCID: PMC10113753
- DOI: 10.1016/j.csbj.2023.03.048
Artificial intelligence and deep learning: New tools for histopathological diagnosis of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease/nonalcoholic steatohepatitis
Abstract
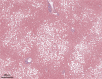
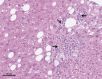
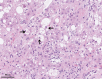
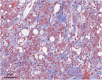
Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD)/nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) is associated with metabolic syndrome and is rapidly increasing globally with the increased prevalence of obesity. Although noninvasive diagnosis of NAFLD/NASH has progressed, pathological evaluation of liver biopsy specimens remains the gold standard for diagnosing NAFLD/NASH. However, the pathological diagnosis of NAFLD/NASH relies on the subjective judgment of the pathologist, resulting in non-negligible interobserver variations. Artificial intelligence (AI) is an emerging tool in pathology to assist diagnoses with high objectivity and accuracy. An increasing number of studies have reported the usefulness of AI in the pathological diagnosis of NAFLD/NASH, and our group has already used it in animal experiments. In this minireview, we first outline the histopathological characteristics of NAFLD/NASH and the basics of AI. Subsequently, we introduce previous research on AI-based pathological diagnosis of NAFLD/NASH.
Keywords: Artificial intelligence; Machine learning; Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease; Nonalcoholic steatohepatitis; Pathological diagnosis.
© 2023 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
We declare that there is no conflict of interest to disclose.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Histopathology of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease/nonalcoholic steatohepatitis.World J Gastroenterol. 2014 Nov 14;20(42):15539-48. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i42.15539. World J Gastroenterol. 2014. PMID: 25400438 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Artificial Intelligence in NAFLD: Will Liver Biopsy Still Be Necessary in the Future?Healthcare (Basel). 2022 Dec 30;11(1):117. doi: 10.3390/healthcare11010117. Healthcare (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36611577 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Artificial intelligence/neural network system for the screening of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and nonalcoholic steatohepatitis.Hepatol Res. 2021 May;51(5):554-569. doi: 10.1111/hepr.13628. Epub 2021 Mar 20. Hepatol Res. 2021. PMID: 33594747
-
Complexity of ballooned hepatocyte feature recognition: Defining a training atlas for artificial intelligence-based imaging in NAFLD.J Hepatol. 2022 May;76(5):1030-1041. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2022.01.011. Epub 2022 Jan 25. J Hepatol. 2022. PMID: 35090960 Free PMC article.
-
[Pediatric nonalcoholic fatty liver disease/nonalcoholic steatohepatitis].Nihon Rinsho. 2012 Oct;70(10):1827-34. Nihon Rinsho. 2012. PMID: 23198569 Review. Japanese.
Cited by
-
Establishing predictive models for malignant and inflammatory pulmonary nodules using clinical data and CT imaging features.Quant Imaging Med Surg. 2025 Apr 1;15(4):2957-2970. doi: 10.21037/qims-24-2338. Epub 2025 Mar 17. Quant Imaging Med Surg. 2025. PMID: 40235774 Free PMC article.
-
Revolutionizing MASLD: How Artificial Intelligence Is Shaping the Future of Liver Care.Cancers (Basel). 2025 Feb 20;17(5):722. doi: 10.3390/cancers17050722. Cancers (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40075570 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Modernizing metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease diagnostics: the progressive shift from liver biopsy to noninvasive techniques.Therap Adv Gastroenterol. 2024 Nov 14;17:17562848241276334. doi: 10.1177/17562848241276334. eCollection 2024. Therap Adv Gastroenterol. 2024. PMID: 39553445 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Diagnostic Value of Hepatic Mast Cell Concentration (MCC) in NAFLD and NASH Severity and Fibrosis Grade.Iran J Pathol. 2024;19(3):291-299. doi: 10.30699/IJP.2024.2016320.3216. Epub 2024 Apr 29. Iran J Pathol. 2024. PMID: 39687460 Free PMC article.
-
Extracellular vesicle-mediated approaches for the diagnosis and therapy of MASLD: current advances and future prospective.Lipids Health Dis. 2025 Jan 7;24(1):5. doi: 10.1186/s12944-024-02396-3. Lipids Health Dis. 2025. PMID: 39773634 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Younossi Z., Tacke F., Arrese M., Sharma B.C., Mostafa I., et al. Global perspectives on nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Hepatology. 2019;69(6):2672–2682. - PubMed
-
- Li J., Zou B., Yeo Y.H., Feng Y., Xie X., et al. Prevalence, incidence, and outcome of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in Asia, 1999-2019: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2019;4(5):389–398. - PubMed
-
- Younossi Z.M., Stepanova M., Ong J., Trimble G., AlQahtani S., et al. Nonalcoholic steatohepatitis is the most rapidly increasing indication for liver transplantation in the United States. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2021;19(3):.. 580-9.e5. - PubMed
-
- Fukusato T., Fukushima J., Shiga J., Takahashi Y., Nakano T., et al. Interobserver variation in the histopathological assessment of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Hepatol Res. 2005;33(2):122–127. - PubMed
-
- Younossi Z.M., Gramlich T., Liu Y.C., Matteoni C., Pertrelli M., et al. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: assessment of variability in pathologic interpretations. Mod Pathol. 1998;11(6):560–565. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
