RIPK1 in the inflammatory response and sepsis: Recent advances, drug discovery and beyond
- PMID: 37090690
- PMCID: PMC10113447
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1114103
RIPK1 in the inflammatory response and sepsis: Recent advances, drug discovery and beyond
Erratum in
-
Corrigendum: RIPK1 in the inflammatory response and sepsis: recent advances, drug discovery and beyond.Front Immunol. 2023 Nov 13;14:1332633. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1332633. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 38022601 Free PMC article.
Abstract
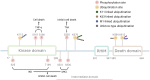
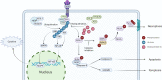
Cytokine storms are an important mechanism of sepsis. TNF-α is an important cytokine. As a regulator of TNF superfamily receptors, RIPK1 not only serves as the basis of the scaffold structure in complex I to promote the activation of the NF-κB and MAPK pathways but also represents an important protein in complex II to promote programmed cell death. Ubiquitination of RIPK1 is an important regulatory function that determines the activation of cellular inflammatory pathways or the activation of death pathways. In this paper, we introduce the regulation of RIPK1, RIPK1 PANoptosome's role in Inflammatory and sepsis, and perspectives.
Keywords: PANoptosis; RIPK1; cytokine storm; inflammatory response; sepsis.
Copyright © 2023 Liu, Tang, Chen, Gao, Zhang and Xiao.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Protein Kinase-Mediated Decision Between the Life and Death.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2021;1275:1-33. doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-49844-3_1. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2021. PMID: 33539010
-
Impaired RIPK1 ubiquitination sensitizes mice to TNF toxicity and inflammatory cell death.Cell Death Differ. 2021 Mar;28(3):985-1000. doi: 10.1038/s41418-020-00629-3. Epub 2020 Sep 30. Cell Death Differ. 2021. PMID: 32999468 Free PMC article.
-
StIKKing it to a death kinase: IKKs prevent TNF-α-induced cell death by phosphorylating RIPK1.Cytokine. 2016 Feb;78:47-50. doi: 10.1016/j.cyto.2015.10.014. Epub 2015 Nov 28. Cytokine. 2016. PMID: 26630177
-
Viral Suppression of RIPK1-Mediated Signaling.mBio. 2021 Aug 31;12(4):e0172321. doi: 10.1128/mBio.01723-21. Epub 2021 Aug 10. mBio. 2021. PMID: 34372694 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Targeting RIPK1 kinase for modulating inflammation in human diseases.Front Immunol. 2023 Mar 8;14:1159743. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1159743. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 36969188 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Association of RIPK1 and RIPK2 Gene Polymorphisms with Rheumatoid Arthritis in a Chinese Han Population.Appl Clin Genet. 2024 Oct 19;17:159-169. doi: 10.2147/TACG.S472418. eCollection 2024. Appl Clin Genet. 2024. PMID: 39444708 Free PMC article.
-
Expression of RIPK-1 and S-100B in traumatic brain injury- exploring a forensic cases series.Int J Legal Med. 2025 May;139(3):1105-1112. doi: 10.1007/s00414-024-03400-2. Epub 2024 Dec 16. Int J Legal Med. 2025. PMID: 39676104
-
Biomarkers of pediatric Epstein-Barr virus-associated hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis through single-cell transcriptomics.Nat Commun. 2025 Jul 25;16(1):6888. doi: 10.1038/s41467-025-62090-5. Nat Commun. 2025. PMID: 40715093 Free PMC article.
-
PANoptosis: Novel insight into regulated cell death and its potential role in cardiovascular diseases (Review).Int J Mol Med. 2024 Sep;54(3):74. doi: 10.3892/ijmm.2024.5398. Epub 2024 Jul 4. Int J Mol Med. 2024. PMID: 38963054 Free PMC article. Review.
-
PANoptosis in cancer, the triangle of cell death.Cancer Med. 2023 Dec;12(24):22206-22223. doi: 10.1002/cam4.6803. Epub 2023 Dec 8. Cancer Med. 2023. PMID: 38069556 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

