A novel mushroom (Auricularia polytricha) glycoprotein protects against lead-induced hepatoxicity, promotes lead adsorption, inhibits organ accumulation of lead, upregulates detoxifying proteins, and enhances immunoregulation in rats
- PMID: 37090774
- PMCID: PMC10116064
- DOI: 10.3389/fnut.2023.1144346
A novel mushroom (Auricularia polytricha) glycoprotein protects against lead-induced hepatoxicity, promotes lead adsorption, inhibits organ accumulation of lead, upregulates detoxifying proteins, and enhances immunoregulation in rats
Abstract
Introduction: Lead is a ubiquitous environmental and industrial pollutant. Its nonbiodegradable toxicity induces a plethora of human diseases. A novel bioactive glycoprotein containing 1.15% carbohydrate, with the ability of adsorbing lead and effecting detoxification, has been purified from Auricularia polytricha and designated as APL. Besides, its mechanisms related to regulation of hepatic metabolic derangements at the proteome level were analyzed in this study.
Methods: Chromatographic techniques were utilized to purify APL in the current study. For investigating the protective effects of APL, Sprague-Dawley rats were given daily intraperitoneal injections of lead acetate for establishment of an animal model, and different dosages of APL were gastrically irrigated for study of protection from lead detoxification. Liver samples were prepared for proteomic analyses to explore the detoxification mechanisms.
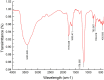
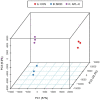
Results and discussion: The detoxifying glycoprotein APL displayed unique molecular properties with molecular weight of 252-kDa, was isolated from fruiting bodies of the edible fungus A. polytricha. The serum concentrations of lead and the liver function biomarkers aspartate and alanine aminotransferases were significantly (p<0.05) improved after APL treatment, as well as following treatment with the positive control EDTA (300 mg/kg body weight). Likewise, results on lead residue showed that the clearance ratios of the liver and kidneys were respectively 44.5% and 18.1% at the dosage of APL 160 mg/kg, which was even better than the corresponding data for EDTA. Proteomics disclosed that 351 proteins were differentially expressed following lead exposure and the expression levels of 41 proteins enriched in pathways mainly involved in cell detoxification and immune regulation were normalized after treatment with APL-H. The results signify that APL ameliorates lead-induced hepatic injury by positive regulation of immune processing, and suggest that APL can be applied as a therapeutic intervention of lead poisoning in clinical practice. This report represents the first demonstration of the protective action of a novel mushroom protein on lead-elicited hepatic toxicity.
Keywords: Auricularia polytricha; detoxification; glycoprotein; lead elimination activity; proteomics.
Copyright © 2023 Zhao, Gao, Wang, Fan, Wang, Zhao, Wong, Wang, Zhao and Ng.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures








Similar articles
-
The Protective Action of the Aqueous Extract of Auricularia polytricha in Paracetamol Induced Hepatotoxicity in Rats.Recent Pat Drug Deliv Formul. 2016;10(1):72-6. doi: 10.2174/1872211309666151030110015. Recent Pat Drug Deliv Formul. 2016. PMID: 26517821
-
Proteomic Analysis Revealed the Fruiting-Body Protein Profile of Auricularia polytricha.Curr Microbiol. 2017 Aug;74(8):943-951. doi: 10.1007/s00284-017-1268-0. Epub 2017 May 29. Curr Microbiol. 2017. PMID: 28555376
-
Lead detoxification of edible fungi Auricularia auricula and Pleurotus ostreatus: the purification of the chelation substances and their effects on rats.Front Nutr. 2023 Apr 20;10:1162110. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2023.1162110. eCollection 2023. Front Nutr. 2023. PMID: 37153916 Free PMC article.
-
[Biosorption of Cd(II), Cu(II), Pb(II) and Zn(II) in aqueous solutions by fruiting bodies of macrofungi (Auricularia polytricha and Tremella fuciformis)].Huan Jing Ke Xue. 2010 Jul;31(7):1566-74. Huan Jing Ke Xue. 2010. PMID: 20825027 Chinese.
-
Final report on the safety assessment of capsicum annuum extract, capsicum annuum fruit extract, capsicum annuum resin, capsicum annuum fruit powder, capsicum frutescens fruit, capsicum frutescens fruit extract, capsicum frutescens resin, and capsaicin.Int J Toxicol. 2007;26 Suppl 1:3-106. doi: 10.1080/10915810601163939. Int J Toxicol. 2007. PMID: 17365137 Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

