Clinical evaluation of a novel multipoint radiofrequency ablation device to treat chronic rhinitis
- PMID: 37090860
- PMCID: PMC10116986
- DOI: 10.1002/lio2.1040
Clinical evaluation of a novel multipoint radiofrequency ablation device to treat chronic rhinitis
Abstract
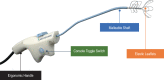
Objective: Safety and efficacy of the NEUROMARK® system for treating chronic rhinitis.
Methods: A prospective, single-arm, multicenter study was performed on adults with chronic rhinitis who underwent radiofrequency ablation to the posterior nasal nerves. Primary endpoints were device-related serious adverse events (SAEs) at 1 month and change from baseline in visual analog scale nasal symptom scale (VAS NSS) for rhinorrhea and nasal congestion at 3 months. Total nasal symptom score (rTNSS) and mini Rhinoconjunctivitis Quality of Life Questionnaire (mini RQLQ) score were also evaluated.
Results: Thirty-six participants were enrolled and completed follow-up at 1 and 3 months. Mean VAS NSS scores for rhinorrhea and nasal congestion demonstrated significant improvement at 3 months (both p < .0001). The mean percent changes from baseline in VAS rhinorrhea and nasal congestion were 53% and 55%, respectively. Total scores and all individual rTNSS items significantly improved (all p < .001) over the measured interval. Percent responder rate (≥30% reduction from baseline in total rTNSS) at 3 months was 78%. The total mean mini RQLQ scores, as well as all subdomains, improved significantly (all p < .0001). At 3 months, 89% of participants reported a minimal clinically important difference of ≥0.4 point improvement in the mini RQLQ score. No SAEs occurred during the study.
Conclusions: The NEUROMARK System is a novel radiofrequency ablation device that provides safe and effective treatment to the posterior nasal nerves for patients with chronic rhinitis. Study participants experienced statistically significant and clinically meaningful improvement in symptoms and quality of life assessments at 3 months post-procedure.
Trial registration: The study is registered at www.clinicaltrials.gov with the unique identifier of NCT05324397.
Level of evidence: 4.
Keywords: congestion; posterior nasal nerve; radiofrequency ablation; rhinitis; rhinorrhea.
© 2023 The Authors. Laryngoscope Investigative Otolaryngology published by Wiley Periodicals LLC on behalf of The Triological Society.
Conflict of interest statement
Douglas D. Reh, Greg Davis, Marc G. Dubin, David M. Yen, and Michael Sillers are medical advisor consultants and Ellen M. O'Malley is a medical writer consultant to Neurent Medical. Kristopher Lay has no conflicts to report.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Long-term outcomes following impedance-controlled radiofrequency ablation for the treatment of chronic rhinitis.Laryngoscope Investig Otolaryngol. 2024 Jun 4;9(3):e1286. doi: 10.1002/lio2.1286. eCollection 2024 Jun. Laryngoscope Investig Otolaryngol. 2024. PMID: 38835333 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical Outcomes After Innovative Multipoint Impedance-Controlled Radiofrequency Ablation of the Posterior Nasal Nerve for Treatment of Chronic Rhinitis.Ear Nose Throat J. 2024 Sep 24:1455613241285134. doi: 10.1177/01455613241285134. Online ahead of print. Ear Nose Throat J. 2024. PMID: 39315465
-
Temperature-controlled radiofrequency ablation for the treatment of chronic rhinitis: Two-year outcomes from a prospective multicenter trial.Int Forum Allergy Rhinol. 2024 Jul;14(7):1182-1194. doi: 10.1002/alr.23315. Epub 2024 Jan 24. Int Forum Allergy Rhinol. 2024. PMID: 38266636 Clinical Trial.
-
Biologics for chronic rhinosinusitis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Mar 12;3(3):CD013513. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013513.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021. PMID: 33710614 Free PMC article.
-
Biologics for chronic rhinosinusitis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 Feb 27;2(2):CD013513. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013513.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Mar 12;3:CD013513. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013513.pub3. PMID: 32102112 Free PMC article. Updated.
Cited by
-
Comparative Effectiveness of Cryotherapy and Radiofrequency Ablation for Chronic Rhinitis: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis.Clin Exp Otorhinolaryngol. 2023 Nov;16(4):369-379. doi: 10.21053/ceo.2023.01214. Epub 2023 Oct 23. Clin Exp Otorhinolaryngol. 2023. PMID: 37871904 Free PMC article.
-
Effectiveness of temperature-controlled radiofrequency neurolysis of the posterior nasal nerve to treat chronic rhinitis: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2024 Feb;281(2):537-545. doi: 10.1007/s00405-023-08242-z. Epub 2023 Sep 20. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2024. PMID: 37728632
-
Long-term outcomes following impedance-controlled radiofrequency ablation for the treatment of chronic rhinitis.Laryngoscope Investig Otolaryngol. 2024 Jun 4;9(3):e1286. doi: 10.1002/lio2.1286. eCollection 2024 Jun. Laryngoscope Investig Otolaryngol. 2024. PMID: 38835333 Free PMC article.
-
Modified technique improves efficacy for in-office posterior nasal nerve ablation.Laryngoscope Investig Otolaryngol. 2024 Mar 25;9(2):e1238. doi: 10.1002/lio2.1238. eCollection 2024 Apr. Laryngoscope Investig Otolaryngol. 2024. PMID: 38529340 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Yan CH, Hwang PH. Surgical management of nonallergic rhinitis. Otolaryngol Clin N Am. 2018;51(5):945‐955. - PubMed
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials