Systemic bevacizumab for pediatric patients with aggressive recurrent respiratory papillomatosis: One single-center experience of eight patients
- PMID: 37090874
- PMCID: PMC10116968
- DOI: 10.1002/lio2.1013
Systemic bevacizumab for pediatric patients with aggressive recurrent respiratory papillomatosis: One single-center experience of eight patients
Abstract
Recurrent respiratory papillomatosis (RRP) is a human papilloma virus (HPV)-driven benign neoplasm, affecting larynx, trachea, and even lung, leading to voice disorders, airway obstruction, and postobstructive pneumonia. Several case reports have documented the promising efficacy of intravenous bevacizumab in reducing the need for surgical intervention among RRP patients. Herein, we present our experience on systemic bevacizumab for pediatric patients with aggressive RRP.
Methods: We retrospectively analyzed clinical, laboratory, radiological, and bronchoscopy findings of pediatric patients with aggressive RRP treated with systemic bevacizumab from July 26, 2021 to March 1, 2022.
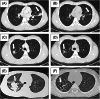
Results: Eight consecutive patients were included. Median age at treatment initiation was 5.5 (range 2.5-8) years old. Twenty-five percentage (2/8) of patients experienced tracheotomy. Pulmonary papilloma was present in 62.5% (5/8) patients. Patients received median 10 cycles of bevacizumab (range 5-12). Patients received initial dosing of 4-7.5 mg/kg every 2-10 weeks of bevacizumab and subsequently extended after achieving the maximum response. None of the patients required surgical intervention during a median 10 (range 8.2-15.4) months follow-up after initiating bevacizumab treatment. Both patients with evaluable lung lesions showed objective response. Only Grade 1 abdominal pain and Grade 1 hyperuricemia were recorded.
Conclusion: Systemic bevacizumab seems to be a well-tolerated and effective treatment option for pediatric patients with aggressive RRP.
Keywords: bevacizumab; efficacy; pediatrics; recurrent respiratory papillomatosis; safety.
© 2023 The Authors. Laryngoscope Investigative Otolaryngology published by Wiley Periodicals LLC on behalf of The Triological Society.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
