Assessment of semicircular canal function in benign paroxysmal positional vertigo using the video head impulse test and caloric test
- PMID: 37090879
- PMCID: PMC10116963
- DOI: 10.1002/lio2.1020
Assessment of semicircular canal function in benign paroxysmal positional vertigo using the video head impulse test and caloric test
Abstract
Objective: To assess semicircular canal function in benign paroxysmal positional vertigo (BPPV) using the video head impulse test (vHIT) and caloric test.
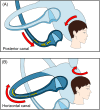
Methods: We retrospectively reviewed 39 patients with idiopathic BPPV who underwent both vHIT and the caloric test. Twenty-one patients had posterior BPPV (p-BPPV) and eighteen had horizontal BPPV (h-BPPV). Vestibulo-ocular reflex (VOR) gain and corrective saccades (CS) were analyzed in vHIT and canal paresis (CP) was calculated in the caloric test.
Results: The mean VOR gain of the posterior canal in p-BPPV was 0.75 ± 0.28 on the affected side, which was significantly smaller than that on the contralateral side (0.93 ± 0.24, p = .00738). On the other hand, there were no significant differences in the VOR gain of the horizontal canal in h-BPPV between the affected and the contralateral sides (p = .769). The rates of the presence of CS were not significantly different between the affected canal and the contralateral canal either in p-BPPV (p = .111) or h-BPPV (p = .0599). The mean CP value in h-BPPV patients (43.5 ± 31.3%) was significantly higher than that in p-BPPV patients (22.2 ± 22.9%; p = .0184).
Conclusion: The VOR gain of vHIT in the affected canal was significantly smaller than that in the contralateral canal in p-BPPV, but not in h-BPPV. The caloric responses of the affected canal are reduced to a significantly larger extent in h-BPPV compared to p-BPPV. These results suggest that BPPV affects the semicircular canal function differently depending on which semicircular canal is involved.
Keywords: BPPV; caloric test; corrective saccade; vHIT; vestibulo‐ocular reflex.
© 2023 The Authors. Laryngoscope Investigative Otolaryngology published by Wiley Periodicals LLC on behalf of The Triological Society.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Vestibulo-Ocular Reflex Abnormalities in Posterior Semicircular Canal Benign Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo: A Pilot Study.Iran J Otorhinolaryngol. 2017 Sep;29(94):269-274. Iran J Otorhinolaryngol. 2017. PMID: 28955674 Free PMC article.
-
Feasibility of Using the Video-Head Impulse Test to Detect the Involved Canal in Benign Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo Presenting With Positional Downbeat Nystagmus.Front Neurol. 2020 Oct 15;11:578588. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2020.578588. eCollection 2020. Front Neurol. 2020. PMID: 33178119 Free PMC article.
-
Presence of corrective saccades in patients with normal vestibulo-ocular reflex gain in video head impulse test.Front Neurol. 2023 Apr 13;14:1152052. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2023.1152052. eCollection 2023. Front Neurol. 2023. PMID: 37122315 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical significance of video head impulse test in benign paroxysmal positional vertigo: a meta-analysis.Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2021 Dec;278(12):4645-4651. doi: 10.1007/s00405-021-06832-3. Epub 2021 Apr 27. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2021. PMID: 33907856 Review.
-
Video head impulse test: a review of the literature.Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2017 Mar;274(3):1215-1222. doi: 10.1007/s00405-016-4157-4. Epub 2016 Jun 21. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2017. PMID: 27328962 Review.
Cited by
-
Otolithic and canal functions assessment during the acute phase of benign paroxysmal positional vertigo.Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2024 May;281(5):2253-2257. doi: 10.1007/s00405-023-08312-2. Epub 2023 Nov 4. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2024. PMID: 37924366
-
Neurological update: neuro-otology 2023.J Neurol. 2023 Dec;270(12):6170-6192. doi: 10.1007/s00415-023-11922-9. Epub 2023 Aug 17. J Neurol. 2023. PMID: 37592138 Free PMC article.
-
Co-Existing Vestibular Hypofunction Impairs Postural Control, but Not Frailty and Well-Being, in Older Adults with Benign Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo.J Clin Med. 2025 Apr 14;14(8):2666. doi: 10.3390/jcm14082666. J Clin Med. 2025. PMID: 40283496 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bhattacharyya N, Baugh RF, Orvidas L, et al. Clinical practice guideline: benign paroxysmal positional vertigo. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2008;139(5 Suppl 4):S47‐S81. - PubMed
-
- Kim JS, Zee DS. Clinical practice. Benign paroxysmal positional vertigo. N Engl J Med. 2014;370(12):1138‐1147. - PubMed
-
- von Brevern M, Bertholon P, Brandt T, et al. Benign paroxysmal positional vertigo: Diagnostic criteria. J Vestib Res. 2015;25(3–4):105‐117. - PubMed
-
- Yang WS, Kim SH, Lee JD, Lee WS. Clinical significance of vestibular evoked myogenic potentials in benign paroxysmal positional vertigo. Otol Neurotol. 2008;29(8):1162‐1166. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
