Establishment and evaluation of a predictive model for length of hospital stay after total knee arthroplasty: A single-center retrospective study in China
- PMID: 37091271
- PMCID: PMC10118006
- DOI: 10.3389/fsurg.2023.1102371
Establishment and evaluation of a predictive model for length of hospital stay after total knee arthroplasty: A single-center retrospective study in China
Abstract
Background: Total knee arthroplasty (TKA) is the ultimate option for end-stage osteoarthritis, and the demand of this procedure are increasing every year. The length of hospital stay (LOS) greatly affects the overall cost of joint arthroplasty. The purpose of this study was to develop and validate a predictive model using perioperative data to estimate the risk of prolonged LOS in patients undergoing TKA.
Methods: Data for 694 patients after TKA collected retrospectively in our department were analyzed by logistic regression models. Multi-variable logistic regression modeling with forward stepwise elimination was used to determine reduced parameters and establish a prediction model. The discrimination efficacy, calibration efficacy, and clinical utility of the prediction model were evaluated.
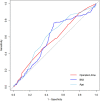
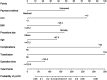
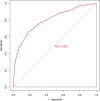
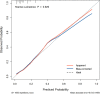
Results: Eight independent predictors were identified: non-medical insurance payment, Charlson Comorbidity Index (CCI) ≥ 3, body mass index (BMI) > 25.2, surgery on Monday, age > 67.5, postoperative complications, blood transfusion, and operation time > 120.5 min had a higher probability of hospitalization for ≥6 days. The model had good discrimination [area under the curve (AUC), 0.802 95% CI, 0.754-0.850]] and good calibration (p = 0.929). A decision curve analysis proved that the nomogram was clinically effective.
Conclusion: This study identified risk factors for prolonged hospital stay in patients after TKA. It is important to recognize all the factors that affect hospital LOS to try to maximize the use of medical resources, optimize hospital LOS and ultimately optimize the care of our patients.
Keywords: length of hospital stay (LOS); nomogram; payment method; prediction model; total knee arthroplasty (TKA).
© 2023 Zhu, Zhang, Sang, Zhao, Wang and Xu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Can machine learning models predict prolonged length of hospital stay following primary total knee arthroplasty based on a national patient cohort data?Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2023 Dec;143(12):7185-7193. doi: 10.1007/s00402-023-05013-7. Epub 2023 Aug 17. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2023. PMID: 37592158
-
Artificial intelligence algorithms accurately predict prolonged length of stay following revision total knee arthroplasty.Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2022 Aug;30(8):2556-2564. doi: 10.1007/s00167-022-06894-8. Epub 2022 Jan 31. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2022. PMID: 35099600
-
Development and validation of a nomogram to predict perioperative blood transfusion in patients undergoing total knee arthroplasty.BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2020 May 20;21(1):315. doi: 10.1186/s12891-020-03328-9. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2020. PMID: 32434505 Free PMC article.
-
Preoperative Patient Factors Affecting Length of Stay following Total Knee Arthroplasty: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.J Arthroplasty. 2019 Sep;34(9):2124-2165.e1. doi: 10.1016/j.arth.2019.04.048. Epub 2019 May 15. J Arthroplasty. 2019. PMID: 31182407
-
Factors associated with hospital stay length, discharge destination, and 30-day readmission rate after primary hip or knee arthroplasty: Retrospective Cohort Study.Orthop Traumatol Surg Res. 2019 Sep;105(5):949-955. doi: 10.1016/j.otsr.2019.04.012. Epub 2019 Jun 15. Orthop Traumatol Surg Res. 2019. PMID: 31208932 Review.
Cited by
-
Development and validation of a nomogram for predicting a forgotten joint in patients one year after robotic-assisted total knee arthroplasty.BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2025 May 31;26(1):536. doi: 10.1186/s12891-025-08789-4. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2025. PMID: 40450270 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

