The impact of comorbidities on interleukin-17 inhibitor therapy in psoriatic arthritis: a Danish population-based cohort study
- PMID: 37091296
- PMCID: PMC10118995
- DOI: 10.1093/rap/rkad035
The impact of comorbidities on interleukin-17 inhibitor therapy in psoriatic arthritis: a Danish population-based cohort study
Abstract
Objective: To investigate the influence of comorbidities on treatment response, disease activity and persistence with first-line IL-17 inhibitor (IL-17i) treatment in patients with PsA.
Methods: Patients were divided into three groups depending on the presence and/or severity of comorbidities using the Charlson Comorbidity Index (CCI). Groups were CCI 0: no comorbidities, CCI 1: one comorbidity and CCI ≥2: two or more comorbidities or one or more severe comorbidities. Outcomes in the groups were compared for treatment persistence, treatment response and disease activity.
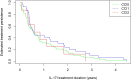
Results: A higher CCI score was associated to an elevation in baseline CRP, swollen joint count and frequency of depression and/or anxiety. The median drug persistence in the groups were CCI 0: 1.8 years, CCI 1: 1.9 years and CCI ≥2: 1.5 years, but was not statistically significant to the CCI score. There were no significant differences in clinical response rates between the groups.
Conclusion: The presence of comorbidities was associated with increased baseline disease activity and frequency of depression and/or anxiety, but was not associated with shorter treatment persistence or lower clinical response rates in a cohort of 155 Danish patients with PsA treated with first-line IL-17i.
Keywords: IL-17 inhibitor; PsA; comorbidities; disease activity; treatment persistence; treatment response.
© The Author(s) 2023. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the British Society for Rheumatology.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Impact of Comorbidities on Tumor Necrosis Factor Inhibitor Therapy in Psoriatic Arthritis: A Population-Based Cohort Study.Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken). 2018 Apr;70(4):592-599. doi: 10.1002/acr.23333. Epub 2018 Mar 7. Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken). 2018. PMID: 28772007
-
Comorbidities, pain and fatigue in psoriatic arthritis, psoriasis and healthy controls: a clinical cohort study.Rheumatology (Oxford). 2021 Jul 1;60(7):3289-3300. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/keaa780. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2021. PMID: 33325531
-
Bristol rheumatoid arthritis fatigue scale is valid in patients with psoriatic arthritis and is associated with overall severe disease and higher comorbidities.Clin Rheumatol. 2020 Jun;39(6):1851-1858. doi: 10.1007/s10067-020-04945-4. Epub 2020 Jan 18. Clin Rheumatol. 2020. PMID: 31955325
-
Long-term persistence of second-line biologics in psoriatic arthritis patients with prior TNF inhibitor exposure: a nationwide cohort study from the French health insurance database (SNDS).RMD Open. 2022 Dec;8(2):e002681. doi: 10.1136/rmdopen-2022-002681. RMD Open. 2022. PMID: 36597983 Free PMC article.
-
Systematic review of mental health comorbidities in psoriatic arthritis.Clin Rheumatol. 2020 Jan;39(1):217-225. doi: 10.1007/s10067-019-04734-8. Epub 2019 Sep 5. Clin Rheumatol. 2020. PMID: 31486931
References
-
- Kristensen LE, Jørgensen TS, Christensen R. et al. Societal costs and patients’ experience of health inequities before and after diagnosis of psoriatic arthritis: a Danish cohort study. Ann Rheum Dis 2017;76:1495–501. - PubMed
-
- Ogdie A, Schwartzman S, Husni ME.. Recognizing and managing comorbidities in psoriatic arthritis. Curr Opin Rheumatol 2015;27:118–26. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous