Perspectives on Usage of Functional Nanomaterials in Antimicrobial Therapy for Antibiotic-Resistant Bacterial Infections
- PMID: 37091369
- PMCID: PMC10116640
- DOI: 10.1021/acsomega.3c00110
Perspectives on Usage of Functional Nanomaterials in Antimicrobial Therapy for Antibiotic-Resistant Bacterial Infections
Abstract
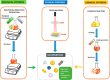
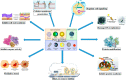
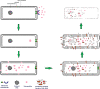
The clinical applications of nanotechnology are emerging as widely popular, particularly as a potential treatment approach for infectious diseases. Diseases associated with multiple drug-resistant organisms (MDROs) are a global concern of morbidity and mortality. The prevalence of infections caused by antibiotic-resistant bacterial strains has increased the urgency associated with researching and developing novel bactericidal medicines or unorthodox methods capable of combating antimicrobial resistance. Nanomaterial-based treatments are promising for treating severe bacterial infections because they bypass antibiotic resistance mechanisms. Nanomaterial-based approaches, especially those that do not rely on small-molecule antimicrobials, display potential since they can bypass drug-resistant bacteria systems. Nanoparticles (NPs) are small enough to pass through the cell membranes of pathogenic bacteria and interfere with essential molecular pathways. They can also target biofilms and eliminate infections that have proven difficult to treat. In this review, we described the antibacterial mechanisms of NPs against bacteria and the parameters involved in targeting established antibiotic resistance and biofilms. Finally, yet importantly, we talked about NPs and the various ways they can be utilized, including as delivery methods, intrinsic antimicrobials, or a mixture.
© 2023 The Authors. Published by American Chemical Society.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Nanomaterials: The New Antimicrobial Magic Bullet.ACS Infect Dis. 2022 Apr 8;8(4):693-712. doi: 10.1021/acsinfecdis.1c00660. Epub 2022 Mar 28. ACS Infect Dis. 2022. PMID: 35343231 Review.
-
Nanoparticles in the Treatment of Infections Caused by Multidrug-Resistant Organisms.Front Pharmacol. 2019 Oct 4;10:1153. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2019.01153. eCollection 2019. Front Pharmacol. 2019. PMID: 31636564 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nanomaterials for alternative antibacterial therapy.Int J Nanomedicine. 2017 Nov 10;12:8211-8225. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S132163. eCollection 2017. Int J Nanomedicine. 2017. PMID: 29184409 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Metal nanobullets for multidrug resistant bacteria and biofilms.Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2014 Nov 30;78:88-104. doi: 10.1016/j.addr.2014.08.004. Epub 2014 Aug 17. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2014. PMID: 25138828 Review.
-
Staphylococcal Bacterial Persister Cells, Biofilms, and Intracellular Infection Are Disrupted by JD1, a Membrane-Damaging Small Molecule.mBio. 2021 Oct 26;12(5):e0180121. doi: 10.1128/mBio.01801-21. Epub 2021 Oct 12. mBio. 2021. PMID: 34634935 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Influence of Physicochemical Properties of Iron Oxide Nanoparticles on Their Antibacterial Activity.ACS Omega. 2024 Jul 25;9(31):33303-33334. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.4c02822. eCollection 2024 Aug 6. ACS Omega. 2024. PMID: 39130596 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nanotherapies based on bacterial metabolism: Mechanisms, design and application.Mater Today Bio. 2025 Jul 18;34:102117. doi: 10.1016/j.mtbio.2025.102117. eCollection 2025 Oct. Mater Today Bio. 2025. PMID: 40735698 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Recent Progress in Terrestrial Biota Derived Antibacterial Agents for Medical Applications.Molecules. 2024 Oct 15;29(20):4889. doi: 10.3390/molecules29204889. Molecules. 2024. PMID: 39459256 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Understanding the mechanisms of antimicrobial resistance and potential therapeutic approaches against the Gram-negative pathogen Acinetobacter baumannii.RSC Med Chem. 2024 Sep 19;15(12):3925-49. doi: 10.1039/d4md00449c. Online ahead of print. RSC Med Chem. 2024. PMID: 39386059 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Unveiling the Potential of Bioinoculants and Nanoparticles in Sustainable Agriculture for Enhanced Plant Growth and Food Security.Biomed Res Int. 2023 Nov 29;2023:6911851. doi: 10.1155/2023/6911851. eCollection 2023. Biomed Res Int. 2023. PMID: 38075309 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Lam S. J.; O’Brien-Simpson N. M.; Pantarat N.; Sulistio A.; Wong E. H. H.; Chen Y. Y.; Lenzo J. C.; Holden J. A.; Blencowe A.; Reynolds E. C.; Qiao G. G. Combating multidrug-resistant Gram-negative bacteria with structurally nanoengineered antimicrobial peptide polymers. Nature. Microbiology 2016, 1, 16162.10.1038/nmicrobiol.2016.162. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Pushparaj Selvadoss P.; Nellore J.; Balaraman Ravindrran M.; Sekar U.; Tippabathani J. Enhancement of antimicrobial activity by liposomal oleic acid-loaded antibiotics for the treatment of multidrug-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Artificial Cells, Nanomedicine and Biotechnology. 2018, 46 (2), 268–73. 10.1080/21691401.2017.1307209. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources