Effect of Annealing on Graphene/PVDF Nanocomposites
- PMID: 37091372
- PMCID: PMC10116551
- DOI: 10.1021/acsomega.3c00283
Effect of Annealing on Graphene/PVDF Nanocomposites
Abstract
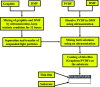
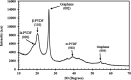
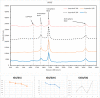
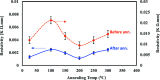
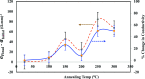
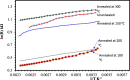
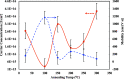
In this study, the process for tuning the electrical properties of graphene/polyvinylidene fluoride (Gr/PVDF) nanocomposite films by a thermal annealing process is explored. The surface morphology and microstructure of the nanocomposite were characterized. The effect of temperature on the electrical conductivity was investigated by heating and cooling the sample from the room temperature up to 150 °C. The effect of annealing on the electrical conductivity was recorded as a function of annealing temperature. A Hall effect measurement was conducted as a function of annealing temperatures to obtain Hall voltage (V H), carrier mobility (μH), carrier concentration (n H), Hall coefficient (R H), resistivity, and carrier conductivity type (n or p). It was found that the films annealed at 150 °C exhibited the best electrical conductivity of Gr/PVDF films. This study may provide an insight into the development and utilization of Gr/PVDF films in future electronics and the potential applications in various sectors such as aerospace, automotive, and biomedical industries.
© 2023 The Authors. Published by American Chemical Society.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures


References
-
- Chung D. D. L. Review Graphite. J. Mater. Sci. 2002, 37, 1475–1489. 10.1023/a:1014915307738. - DOI
-
- Bolotin K. I.; Sikes K. J.; Jiang Z.; Klima M.; Fudenberg G.; Hone J.; Kim P.; Stormer H. Ultrahigh electron mobility in suspended graphene. Solid state communications 2008, 146, 351–355. 10.1016/j.ssc.2008.02.024. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

