Total Chemical Synthesis of Palmitoyl-Conjugated Insulin
- PMID: 37091377
- PMCID: PMC10116525
- DOI: 10.1021/acsomega.2c07918
Total Chemical Synthesis of Palmitoyl-Conjugated Insulin
Abstract
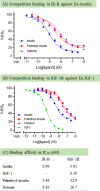
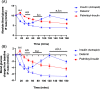
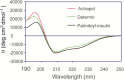
Commercially available insulins are manufactured by recombinant methods for the treatment of diabetes. Long-acting insulin drugs (e.g., detemir and degludec) are obtained by fatty acid conjugation at LysB29 ε-amine of insulin via acid-amide coupling. There are three amine groups in insulin, and they all react with fatty acids in alkaline conditions. Due to the lack of selectivity, such conjugation reactions produce non-desired byproducts. We designed and chemically synthesized a novel thiol-insulin scaffold (CysB29-insulin II), by replacing the LysB29 residue in insulin with the CysB29 residue. Then, we conjugated a fatty acid moiety (palmitic acid, C16) to CysB29-insulin II by a highly efficient and selective thiol-maleimide conjugation reaction. We obtained the target peptide (palmitoyl-insulin) rapidly within 5 min without significant byproducts. The palmitoyl-insulin is shown to be structurally similar to insulin and biologically active both in vitro and in vivo. Importantly, unlike native insulin, palmitoyl-insulin is slow and long-acting.
© 2023 The Authors. Published by American Chemical Society.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Acylation of human insulin with palmitic acid extends the time action of human insulin in diabetic dogs.Diabetes. 1997 Apr;46(4):637-42. doi: 10.2337/diab.46.4.637. Diabetes. 1997. PMID: 9075804
-
Chemical Modification of Insulin Using Flow Chemistry.Chembiochem. 2024 Nov 18;25(22):e202400534. doi: 10.1002/cbic.202400534. Epub 2024 Oct 24. Chembiochem. 2024. PMID: 39166477
-
Basal activity profiles of NPH and [Nepsilon-palmitoyl Lys (B29)] human insulins in subjects with IDDM.Diabetologia. 1998 Jan;41(1):116-20. doi: 10.1007/s001250050876. Diabetologia. 1998. PMID: 9498640
-
Comparative effectiveness and harms of long-acting insulins for type 1 and type 2 diabetes: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Diabetes Obes Metab. 2019 Apr;21(4):984-992. doi: 10.1111/dom.13614. Epub 2019 Jan 22. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2019. PMID: 30552792
-
(Ultra-)long-acting insulin analogues for people with type 1 diabetes mellitus.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Mar 4;3(3):CD013498. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013498.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021. PMID: 33662147 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Site-selective fatty acid chain conjugation of the N-terminus of the recombinant human granulocyte colony-stimulating factor.Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2024 Mar 18;12:1360506. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2024.1360506. eCollection 2024. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2024. PMID: 38576447 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hossain M. A.; Belgi A.; Lin F.; Zhang S.; Shabanpoor F.; Chan L.; Belyea C.; Truong H. T.; Blair A. R.; Andrikopoulos S.; Tregear G. W.; Wade J. D. Use of a temporary “solubilizing” peptide tag for the Fmoc solid-phase synthesis of human insulin glargine via use of regioselective disulfide bond formation. Bioconjugate Chem. 2009, 20, 1390–1396. 10.1021/bc900181a. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Porcellati F.; Lucidi P.; Candeloro P.; Cioli P.; Marinelli Andreoli A.; Curti G.; Bolli G. B.; Fanelli C. G. Pharmacokinetics, pharmacodynamics, and modulation of hepatic glucose production with insulin glargine U300 and glargine U100 at steady state with individualized clinical doses in Type 1 diabetes. Diabetes Care 2019, 42, 85–92. 10.2337/dc18-0706. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

