AI-based radiodiagnosis using chest X-rays: A review
- PMID: 37091458
- PMCID: PMC10116151
- DOI: 10.3389/fdata.2023.1120989
AI-based radiodiagnosis using chest X-rays: A review
Abstract
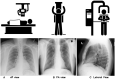
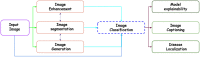
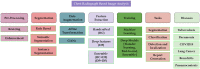
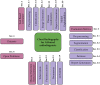
Chest Radiograph or Chest X-ray (CXR) is a common, fast, non-invasive, relatively cheap radiological examination method in medical sciences. CXRs can aid in diagnosing many lung ailments such as Pneumonia, Tuberculosis, Pneumoconiosis, COVID-19, and lung cancer. Apart from other radiological examinations, every year, 2 billion CXRs are performed worldwide. However, the availability of the workforce to handle this amount of workload in hospitals is cumbersome, particularly in developing and low-income nations. Recent advances in AI, particularly in computer vision, have drawn attention to solving challenging medical image analysis problems. Healthcare is one of the areas where AI/ML-based assistive screening/diagnostic aid can play a crucial part in social welfare. However, it faces multiple challenges, such as small sample space, data privacy, poor quality samples, adversarial attacks and most importantly, the model interpretability for reliability on machine intelligence. This paper provides a structured review of the CXR-based analysis for different tasks, lung diseases and, in particular, the challenges faced by AI/ML-based systems for diagnosis. Further, we provide an overview of existing datasets, evaluation metrics for different[][15mm][0mm]Q5 tasks and patents issued. We also present key challenges and open problems in this research domain.
Keywords: COVID-19; Pneumoconiosis; chest X-ray; interpretable deep learning; pneumonia; trusted AI; tuberculosis.
Copyright © 2023 Akhter, Singh and Vatsa.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

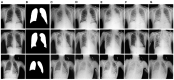
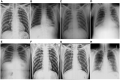
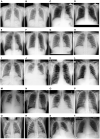
References
-
- Abdullah-Al-Wadud M., Kabir M. H., Dewan M. A. A., Chae O. (2007). A dynamic histogram equalization for image contrast enhancement. IEEE Trans. Consum. Electron. 53, 593–600. 10.1109/TCE.2007.381734 - DOI
-
- Abin D., Thepade S. D., Mankar H., Raut S., Yadav A. (2022). “Blending of contrast enhancement techniques for chest x-ray pneumonia images,” in 2022 International Conference on Electronics and Renewable Systems (ICEARS), 981–985. 10.1109/ICEARS53579.2022.9752286 - DOI
-
- Ahmed F., Hossain E. (2013). Automated facial expression recognition using gradient-based ternary texture patterns. Chin. J. Eng. 2013, 831747. 10.1155/2013/831747 - DOI
-
- Alfadhli F. H. O., Mand A. A., Sayeed M. S., Sim K. S., Al-Shabi M. (2017). “Classification of tuberculosis with surf spatial pyramid features,” in 2017 International Conference on Robotics, Automation and Sciences (ICORAS) (Melaka: IEEE; ), 1–5.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

