Walking Ability, Participation, and Quality of Life in Children with Spastic Diplegic Cerebral Palsy: A Path Analysis Study
- PMID: 37091467
- PMCID: PMC10114265
- DOI: 10.22037/ijcn.v17i1.34924
Walking Ability, Participation, and Quality of Life in Children with Spastic Diplegic Cerebral Palsy: A Path Analysis Study
Abstract
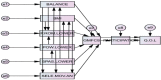
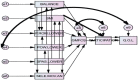
Objectives: This study aims to design a conceptual model for the effect of various factors on walking ability, participation, and quality of life in children with spastic diplegic cerebral palsy (SDCP) and test it based on field data using path analysis.
Materials & methods: This cross-sectional study was performed on 181 children with SDCP. The following were used to measure each of the variables: the Modified Ashworth Scale, the Micro Manual Muscle Tester, the Timed Up and Go Test (TUG), the Boyd and Graham test, the goniometer, weight and height, the Gross Motor Function Classification System, the Life Habits Questionnaire, and cerebral palsy Quality of Life Questionnaire for Children. The structural model was tested in Amos 17.
Results: All paths of the proposed model were significant (P <0.05). Among evaluated variables, muscle strength (B = -0.466), balance (B = 0.326), and spasticity (B = 0.143) affected walking ability. Moreover, as an intermediate factor, walking ability affected the subjects' participation (B = -0.819) and quality of life (B = -0.183).
Conclusion: Muscle strength, balance, and spasticity are the most influential factors in the walking ability of children with SDCP. Furthermore, walking ability and participation are two critical factors in promoting the quality of life of these children.
Keywords: Spastic Diplegic Cerebral Palsyو Walking Abilityو Quality of Lifeو Participationو Structural Equations Modeling.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Path analysis of strength, spasticity, gross motor function, and health-related quality of life in children with spastic cerebral palsy.Health Qual Life Outcomes. 2018 Apr 19;16(1):70. doi: 10.1186/s12955-018-0891-1. Health Qual Life Outcomes. 2018. PMID: 29673348 Free PMC article.
-
Association of muscles length and strength with balance and functional status among children with diplegic spastic cerebral palsy.J Pak Med Assoc. 2023 Feb;73(2):253-257. doi: 10.47391/JPMA.5174. J Pak Med Assoc. 2023. PMID: 36800705
-
Effectiveness of electrical stimulation after administration of botulinum toxin in children with spastic diplegic cerebral palsy: A prospective, randomized clinical study.Turk J Phys Med Rehabil. 2019 Feb 4;65(1):16-23. doi: 10.5606/tftrd.2019.2236. eCollection 2019 Mar. Turk J Phys Med Rehabil. 2019. PMID: 31453540 Free PMC article.
-
Relationships among measures of knee musculoskeletal impairments, gross motor function, and walking efficiency in children with cerebral palsy.Pediatr Phys Ther. 2006 Winter;18(4):253-61. doi: 10.1097/01.pep.0000233054.26082.4e. Pediatr Phys Ther. 2006. PMID: 17108798
-
Association Between Calf Muscle Tone, Plantar Surface Area, and Gross Motor Function in Children with Spastic Diplegic Cerebral Palsy.Int J Gen Med. 2024 Sep 14;17:4037-4044. doi: 10.2147/IJGM.S479557. eCollection 2024. Int J Gen Med. 2024. PMID: 39295857 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
The pilot study of the effect of six-week robot-assisted ankle training on mobility and strength of lower extremity and life habits for children with cerebral palsy.Heliyon. 2024 Jul 10;10(14):e34318. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e34318. eCollection 2024 Jul 30. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 39114037 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Schwabe AL. Comprehensive Care in Cerebral Palsy. Physical medicine and rehabilitation clinics of North America. 2020;31(1):1–13. - PubMed
-
- Rosenbaum P, Paneth N, Leviton A, Goldstein M, Bax M, Damiano D, et al. A report: the definition and classification of cerebral palsy April 2006. Dev Med Child Neurol Suppl. 2007;109(suppl 109):8–14. - PubMed
-
- Schiariti V, Selb M, Cieza A, O'Donnell M. International Classification of Functioning, Disability and Health Core Sets for children and youth with cerebral palsy: a consensus meeting. Developmental Medicine & Child Neurology. 2015;57(2):149–58. - PubMed
-
- Tang-Wai R, Webster RI, Shevell MI. A clinical and etiologic profile of spastic diplegia. Pediatric neurology. 2006;34(3):212–8. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources