Stability of protein particle based Pickering emulsions in various environments: Review on strategies to inhibit coalescence and oxidation
- PMID: 37091511
- PMCID: PMC10113778
- DOI: 10.1016/j.fochx.2023.100651
Stability of protein particle based Pickering emulsions in various environments: Review on strategies to inhibit coalescence and oxidation
Abstract
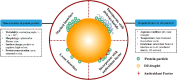
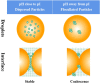
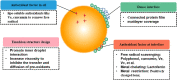
The emerging research interests in fabrication of protein particles as soft-particle emulsifiers show the prospective potential of using protein particles in novel poly-phase dispersing food systems. This review first provides a comprehensive summary and analysis on the dominant role of key physicochemical properties of protein particles including wettability, morphology, surface charge and protein concentration on their emulsifying abilities to construct Pickering emulsions. It was found that the constructed emulsions showed high sensitivity to changes in pH, ionic strength and temperature (thermal and freeze-thaw treatment). Moreover, oxidation remains as a challenge for protein particle based Pickering emulsions during prolonged storage, reducing their acceptance in food products. Current strategies for improving the stability of these emulsions to variable aqueous conditions and variable temperatures, and restricting oxidation event are summarized. In summary, an "ideal" protein particle-based Pickering emulsion system is proposed, encompassing aspects of interfacial property, emulsion network and texture, and antioxidant enrichment, thus promoting industrial translation into novel food and nutraceutical products.
Keywords: Interface; Oxidation; Pickering Emulsion; Protein particle; Stability.
© 2023 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Fabrication and Characterization of Quinoa Protein Nanoparticle-Stabilized Food-Grade Pickering Emulsions with Ultrasound Treatment: Effect of Ionic Strength on the Freeze-Thaw Stability.J Agric Food Chem. 2018 Aug 8;66(31):8363-8370. doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.8b02407. Epub 2018 Jul 24. J Agric Food Chem. 2018. PMID: 30016098
-
The influence of ionic strength on the characteristics of heat-induced soy protein aggregate nanoparticles and the freeze-thaw stability of the resultant Pickering emulsions.Food Funct. 2017 Aug 1;8(8):2974-2981. doi: 10.1039/c7fo00616k. Epub 2017 Jul 26. Food Funct. 2017. PMID: 28745770
-
Structure and properties of Pickering emulsions stabilized solely with novel buckwheat protein colloidal particles.Int J Biol Macromol. 2023 Jan 31;226:61-71. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2022.12.047. Epub 2022 Dec 7. Int J Biol Macromol. 2023. PMID: 36493922
-
Advances in Pickering emulsions stabilized by protein particles: Toward particle fabrication, interaction and arrangement.Food Res Int. 2022 Jul;157:111380. doi: 10.1016/j.foodres.2022.111380. Epub 2022 May 14. Food Res Int. 2022. PMID: 35761636 Review.
-
Tuning Amphiphilicity of Particles for Controllable Pickering Emulsion.Materials (Basel). 2016 Nov 8;9(11):903. doi: 10.3390/ma9110903. Materials (Basel). 2016. PMID: 28774029 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Research progress on plant-based protein Pickering particles: Stabilization mechanisms, preparation methods, and application prospects in the food industry.Food Chem X. 2023 Dec 13;21:101066. doi: 10.1016/j.fochx.2023.101066. eCollection 2024 Mar 30. Food Chem X. 2023. PMID: 38268843 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Advances in emulsion stability: A review on mechanisms, role of emulsifiers, and applications in food.Food Chem X. 2025 Jul 17;29:102792. doi: 10.1016/j.fochx.2025.102792. eCollection 2025 Jul. Food Chem X. 2025. PMID: 40747487 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Biocompatible Pickering Emulsions from Andrias davidianus Byproducts for Promoting Burn Wound Healing.Biomater Res. 2025 Aug 19;29:0233. doi: 10.34133/bmr.0233. eCollection 2025. Biomater Res. 2025. PMID: 40836952 Free PMC article.
-
Soy Protein-Based Emulsions: Application as Lipid Substitutes in Surimi Gels.Foods. 2025 Jul 1;14(13):2342. doi: 10.3390/foods14132342. Foods. 2025. PMID: 40647094 Free PMC article.
-
Formulation and Stability of Quercetin-Loaded Pickering Emulsions Using Chitosan/Gum Arabic Nanoparticles for Topical Skincare Applications.Polymers (Basel). 2025 Jul 4;17(13):1871. doi: 10.3390/polym17131871. Polymers (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40647880 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Amagliani L., Schmitt C. Globular plant protein aggregates for stabilization of food foams and emulsions. Trends in Food Science & Technology. 2017;67:248–259.
-
- Berton C., Schroen K. Pickering emulsions for food applications: Background, trends, and challenges. Annual Review of Food Science and Technology. 2015;6:263–297. - PubMed
-
- Berton C., Ropers H., Guibert D., Sole V., Genot C. Modifications of interfacial proteins in oil-in-water emulsions prior to and during lipid oxidation. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry. 2012;60(35):8659–8671. - PubMed
-
- Binks B., Lumsdon S. Pickering emulsions stabilized by monodisperse latex particles: Effects of particle size. Langmuir. 2001;17(15):4540–4547.
-
- Chang C., Niu F., Gu L., Li X., Yang H., Zhou B.…Yang Y. Formation of fibrous or granular egg white protein microparticles and properties of the integrated emulsions. Food Hydrocolloids. 2016;61:477–486.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

