Correlation and predictive ability of sensory characteristics and social interaction in children with autism spectrum disorder
- PMID: 37091701
- PMCID: PMC10117963
- DOI: 10.3389/fpsyt.2023.1056051
Correlation and predictive ability of sensory characteristics and social interaction in children with autism spectrum disorder
Abstract
Background: Individuals with autism spectrum disorder (ASD) often have different social characteristics and particular sensory processing patterns, and these sensory behaviors may affect their social functioning. The objective of our study is to investigate the sensory profiles of children with ASD and their association with social behavior. Specifically, we aim to identify the predictive role of sensory processing in social functioning.
Methods: The Short Sensory Profile (SSP) was utilized to analyze sensory differences between ASD children and their peers. The Social Responsiveness Scale (SRS) and other clinical scales were employed to assess the social functioning of children with ASD. Additionally, the predictive ability of sensory perception on social performance was discussed using random forest and support vector machine (SVM) models.
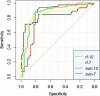
Results: The SSP scores of ASD children were lower than those of the control group, and there was a significant negative correlation between SSP scores and clinical scale scores (P < 0.05). The random forest and SVM models, using all the features, showed higher sensitivity, while the random forest model with 7-feature factors had the highest specificity. The area under the receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve (AUC) for all the models was higher than 0.8.
Conclusion: Autistic children in our study have different patterns of sensory processing than their peers, which are significantly related to their patterns of social functioning. Sensory features can serve as a good predictor of social functioning in individuals with ASD.
Keywords: SSP; autism; clinical scale; core symptom; sensory; social.
Copyright © 2023 Zhai, Li, Zhou, Fan, Xia, Wang, Li, Hou, Wang and Wu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Similar articles
-
The reliability and validity of the social responsiveness scale to measure autism symptomology in Vietnamese children.Autism Res. 2019 Nov;12(11):1706-1718. doi: 10.1002/aur.2179. Epub 2019 Jul 29. Autism Res. 2019. PMID: 31355545 Free PMC article.
-
Impaired lipid metabolism markers to assess the risk of neuroinflammation in autism spectrum disorder.Metab Brain Dis. 2018 Aug;33(4):1141-1153. doi: 10.1007/s11011-018-0206-6. Epub 2018 Mar 22. Metab Brain Dis. 2018. PMID: 29569150
-
Sensory processing profiles and autistic symptoms as predictive factors in autism spectrum disorder and Williams syndrome.J Intellect Disabil Res. 2020 Aug;64(8):657-665. doi: 10.1111/jir.12738. Epub 2020 May 13. J Intellect Disabil Res. 2020. PMID: 32400919
-
A Review of Machine Learning Methods of Feature Selection and Classification for Autism Spectrum Disorder.Brain Sci. 2020 Dec 7;10(12):949. doi: 10.3390/brainsci10120949. Brain Sci. 2020. PMID: 33297436 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Sensory Processing Differences in Individuals With Autism Spectrum Disorder: A Narrative Review of Underlying Mechanisms and Sensory-Based Interventions.Cureus. 2023 Oct 31;15(10):e48020. doi: 10.7759/cureus.48020. eCollection 2023 Oct. Cureus. 2023. PMID: 38034138 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Decoding the genetic landscape of autism: A comprehensive review.World J Clin Pediatr. 2024 Sep 9;13(3):98468. doi: 10.5409/wjcp.v13.i3.98468. eCollection 2024 Sep 9. World J Clin Pediatr. 2024. PMID: 39350903 Free PMC article.
References
-
- American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders. 5th ed. Washington, D.C: American Psychiatric Association; (2013). 10.1176/appi.books.9780890425596 - DOI
-
- Baio J, Wiggins L, Christensen DL, Maenner M, Warren Z, Kurzius-Spencer M, et al. Prevalence of autism spectrum disorder among children aged 8 years - autism and developmental disabilities monitoring network, 11 sites, United States, 2014. MMWR Surveill Summ. (2018) 67:1–23. 10.15585/mmwr.ss6706a1 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- World Health Organization (WHO). Autism spectrum disorders. Geneva: World Health Organization; (2019).
-
- Kanner L. Autistic disturbances of affective contact. Acta Paedops. (1968) 35: 100–36. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources