Increase in prevalence of Streptococcus pneumoniae serogroup 24 in children upon introducing 13-valent pneumococcal conjugate vaccine in Japan
- PMID: 37091738
- PMCID: PMC10118250
- DOI: 10.1099/acmi.0.000507.v3
Increase in prevalence of Streptococcus pneumoniae serogroup 24 in children upon introducing 13-valent pneumococcal conjugate vaccine in Japan
Abstract
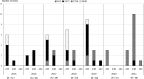
After introducing the 13-valent pneumococcal conjugate vaccine (PCV13) for children, a change in the prevalence of different Streptococcus pneumoniae serotypes that cause invasive pneumococcal diseases (IPDs) has been observed. The prevalence of vaccine serotypes has decreased and that of non-vaccine serotypes has increased. Currently, serogroup 24 has become one of the major non-vaccine serotypes causing IPDs in children in Japan. The aim of this study was to characterize clinical and genomic features of S. pneumoniae serogroup 24 strains isolated from sterile body sites in Japanese children. Serotyping, multi-locus sequence typing and genomic analysis of capsular polysaccharides of 61 strains of serogroup 24 were performed from 2015 to 2021. Among the 61 strains, 36, 23 and two belonged to serotypes 24F, 24B and 24C, respectively. The 24F sequence type (ST) 2572 and 24B ST 2572 were the major serotypes and sequence types observed from 2015 to 2019. By contrast, 24F ST 162 and 24B ST 2754 were the two major serotypes and sequence types observed after 2020. Two strains of serotype 24C were detected for the first time in Japan. Sequence analysis of the abpA gene, which plays a role in the synthesis of capsular polysaccharides in S. pneumoniae , was performed to distinguish different strains of serogroup 24. After the introduction of PCV13 in Japan, serogroup 24 has become one of the most prevalent non-vaccine serotypes causing IPDs in children. This serogroup has not been targeted in the next-generation pneumococcal conjugate vaccines. Therefore, monitoring of S. pneumoniae serogroup 24 that causes IPDs in children is essential.
Keywords: Streptococcus pneumoniae; abpAgene; sequence type; serogroup 24.
© 2023 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Clinical and Bacteriological Analysis of Pediatric Pneumococcal Meningitis after 13-Valent Pneumococcal Conjugate Vaccine Introduction in Japan.Microbiol Spectr. 2022 Apr 27;10(2):e0182221. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.01822-21. Epub 2022 Mar 31. Microbiol Spectr. 2022. PMID: 35357224 Free PMC article.
-
Structural, Genetic, and Serological Elucidation of Streptococcus pneumoniae Serogroup 24 Serotypes: Discovery of a New Serotype, 24C, with a Variable Capsule Structure.J Clin Microbiol. 2021 Jun 18;59(7):e0054021. doi: 10.1128/JCM.00540-21. Epub 2021 Jun 18. J Clin Microbiol. 2021. PMID: 33883183 Free PMC article.
-
Serotype distribution and antimicrobial susceptibility of Streptococcus pneumoniae strains isolated in Japan after introduction of the routine immunization program.J Infect Chemother. 2017 Apr;23(4):234-240. doi: 10.1016/j.jiac.2016.12.016. Epub 2017 Feb 1. J Infect Chemother. 2017. PMID: 28161295
-
Pneumococcal serotype evolution in Western Europe.BMC Infect Dis. 2015 Oct 14;15:419. doi: 10.1186/s12879-015-1147-x. BMC Infect Dis. 2015. PMID: 26468008 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A systematic review of invasive pneumococcal disease vaccine failures and breakthrough with higher-valency pneumococcal conjugate vaccines in children.Expert Rev Vaccines. 2022 Feb;21(2):201-214. doi: 10.1080/14760584.2022.2012455. Epub 2022 Feb 3. Expert Rev Vaccines. 2022. PMID: 34882050
Cited by
-
Invasive pneumococcal disease caused by non-vaccine Streptococcus pneumoniae serotype 24B in an immunocompetent child.Radiol Case Rep. 2024 Feb 3;19(4):1642-1645. doi: 10.1016/j.radcr.2024.01.048. eCollection 2024 Apr. Radiol Case Rep. 2024. PMID: 38327552 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention Pneumococcal disease-Types of infection 2020. https://www.cdc.gov/pneumococcal/about/infection-types.html n.d.
-
- Kobayashi M, Farrar JL, Gierke R, Britton A, Childs L, et al. Use of 15-valent pneumococcal conjugate vaccine and 20-valent pneumococcal conjugate vaccine among U.S. adults: updated recommendations of the advisory committee on immunization practices - United States, 2022. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2022;71:109–117. doi: 10.15585/mmwr.mm7104a1. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
