Bioinformatics analysis based on crucial genes of endothelial cells in rheumatoid
- PMID: 37091794
- PMCID: PMC10117816
- DOI: 10.3389/fgene.2023.1143644
Bioinformatics analysis based on crucial genes of endothelial cells in rheumatoid
Retraction in
-
Retraction: Bioinformatics analysis based on crucial genes of endothelial cells in rheumatoid.Front Genet. 2024 Feb 9;15:1380892. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2024.1380892. eCollection 2024. Front Genet. 2024. PMID: 38404669 Free PMC article.
Abstract
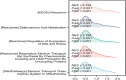
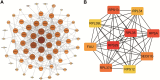
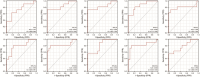
Objectives: Synovial neovascularization is an early and remarkable event that promotes the development of rheumatoid arthritis (RA) synovial hyperplasia. This study aimed to find potential diagnostic markers and molecular therapeutic targets for RA at the mRNA molecular level. Method: We download the expression profile dataset GSE46687 from the gene expression ontology (GEO) microarray, and used R software to screen out the differentially expressed genes between the normal group and the disease group. Then we performed functional enrichment analysis, used the STRING database to construct a protein-protein interaction (PPI) network, and identify candidate crucial genes, infiltration of the immune cells and targeted molecular drug. Results: Rheumatoid arthritis datasets included 113 differentially expressed genes (DEGs) including 104 upregulated and 9 downregulated DEGs. The enrichment analysis of genes shows that the differential genes are mainly enriched in condensed chromosomes, ribosomal subunits, and oxidative phosphorylation. Through PPI network analysis, seven crucial genes were identified: RPS13, RPL34, RPS29, RPL35, SEC61G, RPL39L, and RPL37A. Finally, we find the potential compound drug for RA. Conclusion: Through this method, the pathogenesis of RA endothelial cells was further explained. It provided new therapeutic targets, but the relationship between these genes and RA needs further research to be validated in the future.
Keywords: DEGs; bioinformatics; endothelial cells; gene expression Omnibus; rheumatoid arthritis.
Copyright © 2023 Zhou and Wu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Screening and identification of potential hub genes and immune cell infiltration in the synovial tissue of rheumatoid arthritis by bioinformatic approach.Heliyon. 2023 Jan 10;9(1):e12799. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e12799. eCollection 2023 Jan. Heliyon. 2023. PMID: 36699262 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of Candidate Genes Related to Synovial Macrophages in Rheumatoid Arthritis by Bioinformatics Analysis.Int J Gen Med. 2021 Nov 4;14:7687-7697. doi: 10.2147/IJGM.S333512. eCollection 2021. Int J Gen Med. 2021. PMID: 34764682 Free PMC article.
-
Three hematologic/immune system-specific expressed genes are considered as the potential biomarkers for the diagnosis of early rheumatoid arthritis through bioinformatics analysis.J Transl Med. 2021 Jan 6;19(1):18. doi: 10.1186/s12967-020-02689-y. J Transl Med. 2021. PMID: 33407587 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of differentially expressed genes, signaling pathways and immune infiltration in rheumatoid arthritis by integrated bioinformatics analysis.Hereditas. 2021 Jan 4;158(1):5. doi: 10.1186/s41065-020-00169-3. Hereditas. 2021. PMID: 33397492 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of differential key biomarkers in the synovial tissue between rheumatoid arthritis and osteoarthritis using bioinformatics analysis.Clin Rheumatol. 2021 Dec;40(12):5103-5110. doi: 10.1007/s10067-021-05825-1. Epub 2021 Jul 5. Clin Rheumatol. 2021. PMID: 34224029
Cited by
-
Identification of differentially expressed genes, signaling pathways and immune infiltration in postmenopausal osteoporosis by integrated bioinformatics analysis.Heliyon. 2023 Dec 16;10(1):e23794. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e23794. eCollection 2024 Jan 15. Heliyon. 2023. PMID: 38205281 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

