Anoikis in phenotypic reprogramming of the prostate tumor microenvironment
- PMID: 37091854
- PMCID: PMC10113530
- DOI: 10.3389/fendo.2023.1160267
Anoikis in phenotypic reprogramming of the prostate tumor microenvironment
Abstract
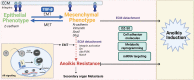
Prostate cancer is one of the most common malignancies in males wherein 1 in 8 men are diagnosed with this disease in their lifetime. The urgency to find novel therapeutic interventions is associated with high treatment resistance and mortality rates associated with castration-resistant prostate cancer. Anoikis is an apoptotic phenomenon for normal epithelial or endothelial cells that have lost their attachment to the extracellular matrix (ECM). Tumor cells that lose their connection to the ECM can die via apoptosis or survive via anoikis resistance and thus escaping to distant organs for metastatic progression. This review discusses the recent advances made in our understanding of the signaling effectors of anoikis in prostate cancer and the approaches to translate these mechanistic insights into therapeutic benefits for reducing lethal disease outcomes (by overcoming anoikis resistance). The prostate tumor microenvironment is a highly dynamic landscape wherein the balance between androgen signaling, cell lineage changes, epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT), extracellular matrix interactions, actin cytoskeleton remodeling as well as metabolic changes, confer anoikis resistance and metastatic spread. Thus, these mechanisms also offer unique molecular treatment signatures, exploitation of which can prime prostate tumors to anoikis induction with a high translational significance.
Keywords: EMT; anoikis; extracellular matrix; metastasis; phenotypic reprogramming; prostate cancer; treatment resistance.
Copyright © 2023 Nepali and Kyprianou.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Anoikis and survival connections in the tumor microenvironment: is there a role in prostate cancer metastasis?Cancer Res. 2005 Dec 15;65(24):11230-5. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-05-2763. Cancer Res. 2005. PMID: 16357123 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cell death under epithelial-mesenchymal transition control in prostate cancer therapeutic response.Int J Urol. 2018 Apr;25(4):318-326. doi: 10.1111/iju.13505. Epub 2018 Jan 17. Int J Urol. 2018. PMID: 29345000 Review.
-
Profiling Prostate Cancer Therapeutic Resistance.Int J Mol Sci. 2018 Mar 19;19(3):904. doi: 10.3390/ijms19030904. Int J Mol Sci. 2018. PMID: 29562686 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Targeting anoikis resistance in prostate cancer metastasis.Mol Aspects Med. 2010 Apr;31(2):205-14. doi: 10.1016/j.mam.2010.02.001. Epub 2010 Feb 11. Mol Aspects Med. 2010. PMID: 20153362 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Anoikis and EMT: Lethal "Liaisons" during Cancer Progression.Crit Rev Oncog. 2016;21(3-4):155-168. doi: 10.1615/CritRevOncog.2016016955. Crit Rev Oncog. 2016. PMID: 27915969 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Obesity, dietary interventions and microbiome alterations in the development and progression of prostate cancer.Front Immunol. 2025 Jan 7;15:1448116. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1448116. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2025. PMID: 39840030 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Identification of Anoikis-Related Genes in Chronic Kidney Disease Based on Bioinformatics Analysis Combined with Experimental Validation.J Inflamm Res. 2025 Jan 21;18:973-994. doi: 10.2147/JIR.S498820. eCollection 2025. J Inflamm Res. 2025. PMID: 39867944 Free PMC article.
-
Epithelial-mesenchymal plasticity in cancer: signaling pathways and therapeutic targets.MedComm (2020). 2024 Aug 1;5(8):e659. doi: 10.1002/mco2.659. eCollection 2024 Aug. MedComm (2020). 2024. PMID: 39092293 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Anoikis-Related Genes Impact Prognosis and Tumor Microenvironment in Bladder Cancer.Mol Biotechnol. 2025 Aug;67(8):3268-3280. doi: 10.1007/s12033-024-01255-x. Epub 2024 Aug 22. Mol Biotechnol. 2025. PMID: 39172330
-
Integrative analysis of Anoikis-related genes reveals that FASN is a novel prognostic biomarker and promotes the malignancy of bladder cancer via Wnt/β-catenin pathway.Heliyon. 2024 Jul 3;10(13):e34029. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e34029. eCollection 2024 Jul 15. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 39071712 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Zhang P, Song Y, Sun Y, Li X, Chen L, Yang L, et al. . AMPK/GSK3β/β-catenin cascade-triggered overexpression of CEMIP promotes migration and invasion in anoikis-resistant prostate cancer cells by enhancing metabolic reprogramming. FASEB J (2018) 32(7):3924–35. doi: 10.1096/fj.201701078R - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

