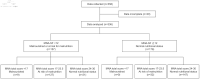
Nutritional Status in Patients Undergoing Phase II Cardiac Rehabilitation by Mini Nutritional Assessment
- PMID: 37091881
- PMCID: PMC10116935
- DOI: 10.14740/cr1479
Nutritional Status in Patients Undergoing Phase II Cardiac Rehabilitation by Mini Nutritional Assessment
Abstract
Background: Malnutrition impairs quality of life and prognosis of patients with cardiovascular disease. The Mini Nutritional Assessment (MNA) is a screening tool developed for the nutritional assessment of older adults. However, usefulness of MNA for patients undergoing cardiac rehabilitation (CR) has not been fully investigated.
Methods: From March 2017 to September 2019, the MNA-short form (MNA-SF) and the MNA total score in patients undergoing phase II CR at the Juntendo University Hospital were evaluated.
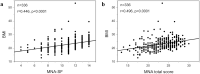
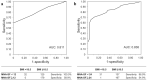
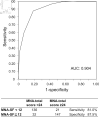
Results: A total of 336 patients (mean age 70.1 ± 11.4 years; males: 209) were analyzed. In the MNA-SF, 157 patients (47%) were found to be malnourished or at risk of malnutrition. In MNA total score, 168 patients (50%) were found to be malnourished or at risk of malnutrition. The MNA-SF < 12 group had significantly lower body mass index (BMI), hemoglobin level, low MNA scores for protein/water intake, self-evaluation of nutrition and health, and upper arm and calf circumferences compared to the MNA-SF ≥ 12 group. Assuming BMI < 18.5 as malnutrition, the sensitivity and specificity for malnutrition were 100% and 58.9% for MNA-SF, and 96.9% and 54.9% for MNA total score, respectively.
Conclusions: MNA is useful in screening for malnutrition in patients undergoing CR. Approximately 50% of them were determined to be malnourished or at risk of malnutrition, suggesting the need for detailed evaluation regarding their food intake and dietary intervention.
Keywords: Cardiac rehabilitation; Malnutrition; Mini Nutritional Assessment; Screening.
Copyright 2023, Nozawa et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Beyond malnutrition screening: appropriate methods to guide nutrition care for aged care residents.J Acad Nutr Diet. 2012 Mar;112(3):376-81. doi: 10.1016/j.jada.2011.09.038. Epub 2012 Mar 1. J Acad Nutr Diet. 2012. PMID: 22717197
-
Comparison of two nutrition assessment tools in surgical elderly inpatients in Northern China.Nutr J. 2015 Jul 14;14:68. doi: 10.1186/s12937-015-0054-8. Nutr J. 2015. PMID: 26170020 Free PMC article.
-
Prevalence of malnutrition diagnosed by the Global Leadership Initiative on Malnutrition and Mini Nutritional Assessment in older adult outpatients and comparison between the Global Leadership Initiative on Malnutrition and Mini Nutritional Assessment energy-protein intake: A cross-sectional study.JPEN J Parenter Enteral Nutr. 2022 Feb;46(2):367-377. doi: 10.1002/jpen.2123. Epub 2021 May 27. JPEN J Parenter Enteral Nutr. 2022. PMID: 33893657
-
Identifying the elderly at risk for malnutrition. The Mini Nutritional Assessment.Clin Geriatr Med. 2002 Nov;18(4):737-57. doi: 10.1016/s0749-0690(02)00059-9. Clin Geriatr Med. 2002. PMID: 12608501 Review.
-
Validity of Nutritional Screening Tools for Community-Dwelling Older Adults: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.J Am Med Dir Assoc. 2019 Oct;20(10):1351.e13-1351.e25. doi: 10.1016/j.jamda.2019.06.024. Epub 2019 Aug 10. J Am Med Dir Assoc. 2019. PMID: 31409560
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
