Citizen Science Informs How Missourians Interact With Ticks
- PMID: 37091933
- PMCID: PMC10121117
Citizen Science Informs How Missourians Interact With Ticks
Abstract
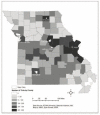
Understanding which tick species Missourians interact with and where exposures occur can help prevent and diagnose tickborne diseases. A statewide survey of ticks and tickborne pathogens was conducted using citizen science. Missourians submitted 12,819 ticks from April-December 2021. In total, 71% of ticks were Amblyomma americanum, and 89% were collected from a person or a pet. These preliminary data provide tick distributions at the county level and identify patterns of direct tick exposure to humans.
Copyright 2023 by the Missouri State Medical Association.
Figures
References
-
- Bacon RM, Pilgard MA, Johnson BJ, Piesman J, Biggerstaff BJ, Quintana M. Rapid detection methods and prevalence estimation for Borrelia lonestari glpQ in Amblyomma americanum (Acari: Ixodidae) pools of unequal size. Vector Borne Zoonotic Dis. 2005;5(2):146–156. doi: 10.1089/vbz.2005.5.146. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Berrada ZL, Goethert HK, Telford SR. Isolation of Francisella tularensis tularensis subpopulation A.I from Missouri lone star ticks. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2008;79:781.
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous