Absence of Nkx2-3 induces ectopic lymphatic endothelial differentiation associated with impaired extramedullary stress hematopoiesis in the spleen
- PMID: 37091975
- PMCID: PMC10113473
- DOI: 10.3389/fcell.2023.1170389
Absence of Nkx2-3 induces ectopic lymphatic endothelial differentiation associated with impaired extramedullary stress hematopoiesis in the spleen
Abstract
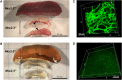
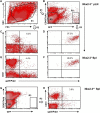
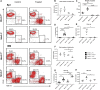
The red and white pulps as two main parts of the spleen are arranged around distinct types of vasculature, and perform significantly different functions in both humans and mice. Previous observations indicated a profound alteration of the local vessel specialization in mice lacking Nkx2-3 homeodomain transcription factor, including contradictory results suggesting presence of an ectopic lymphatic vascular structure. Furthermore, how the absence of Nkx2-3 and the consequential changes in endothelial components affect the extramedullary hematopoietic activity restricted to the splenic red pulp is unknown. In this work, we investigated the role of Nkx2-3 homeodomain transcription factor as a major morphogenic determinant for vascular specification, and its effect in the extramedullary hematopoiesis following acute blood loss and pharmacological stimulation of megakaryocyte differentiation after treatment with thrombopoietin-receptor mimetic Romiplostim. We found that, in mice lacking Nkx2-3, Prox1-positive lymphatic capillaries containing gp38/CD31 double positive lymphatic endothelial cells develop, arranged into an extensive meshwork, while the Clever1-positive venous segments of red pulp blood vasculature are absent. This lymphatic endothelial shift is coupled with a severely compromised splenic erythropoiesis and a significantly reduced splenic megakaryocyte colony formation following Romiplostim treatment in mice lacking Nkx2-3. These findings indicate that the shift of microvascular patterning in the absence of Nkx2-3 includes the emergence of ectopic Prox1-positive lymphatic vessels, and that this pivoting towards lymph node-like vascular patterning is associated with an impaired reserve hematopoietic capacity of the splenic red pulp.
Keywords: NKX2-3; Prox1; hematopoiesis; lymphatic endothelium; spleen; stroma.
Copyright © 2023 Gábris, Kiss, Szirmay, Szomor, Berta, Jakus, Kellermayer and Balogh.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Absence of Nkx2-3 homeodomain transcription factor induces the formation of LYVE-1-positive endothelial cysts without lymphatic commitment in the spleen.J Histochem Cytochem. 2011 Jul;59(7):690-700. doi: 10.1369/0022155411410061. J Histochem Cytochem. 2011. PMID: 21705651 Free PMC article.
-
Transcription factor Nkx2-3 controls the vascular identity and lymphocyte homing in the spleen.J Immunol. 2011 Jun 15;186(12):6981-9. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1003770. Epub 2011 May 18. J Immunol. 2011. PMID: 21593383
-
Distinct roles of lymphotoxin-beta signaling and the homeodomain transcription factor Nkx2.3 in the ontogeny of endothelial compartments in spleen.Cell Tissue Res. 2007 Jun;328(3):473-86. doi: 10.1007/s00441-007-0378-6. Epub 2007 Feb 21. Cell Tissue Res. 2007. PMID: 17318587
-
Human spleen microanatomy: why mice do not suffice.Immunology. 2015 Jul;145(3):334-46. doi: 10.1111/imm.12469. Immunology. 2015. PMID: 25827019 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Prox1, master regulator of the lymphatic vasculature phenotype.Cell Tissue Res. 2003 Oct;314(1):85-92. doi: 10.1007/s00441-003-0747-8. Epub 2003 Jul 22. Cell Tissue Res. 2003. PMID: 12883994 Review.
Cited by
-
Human ectodermal organoids reveal the cellular origin of DiGeorge Syndrome.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2025 Aug 8:2025.08.08.669417. doi: 10.1101/2025.08.08.669417. bioRxiv. 2025. PMID: 40855884 Free PMC article. Preprint.
-
Spleen granulopoiesis in psoriasis immune microenvironment aggravates psoriasis via IL-6/P-STAT3 signaling.Biol Direct. 2025 Sep 2;20(1):96. doi: 10.1186/s13062-025-00675-2. Biol Direct. 2025. PMID: 40890773 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bellomo A., Mondor I., Spinelli L., Lagueyrie M., Stewart B. J., Brouilly N., et al. (2020). Reticular fibroblasts expressing the transcription factor WT1 define a stromal niche that maintains and replenishes splenic red pulp macrophages. Immunity 53, 127–142.e7. 10.1016/j.immuni.2020.06.008 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

