A reference interval study of serum 25-Hydroxyvitamin D among an African elderly population
- PMID: 37092041
- PMCID: PMC10117474
- DOI: 10.4314/ahs.v22i4.27
A reference interval study of serum 25-Hydroxyvitamin D among an African elderly population
Abstract
Background: Elderly people have increased risk factors for low serum vitamin D levels, which is worsened among the black race. Therefore, elderly Africans constitute a reference population for vitamin D study.
Aim: The aim of this study was to establish the reference interval of serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D (25(OH)D) among an African elderly population.
Methodology: This was a cross-sectional study of rural community dwellers in Enugu, south-eastern Nigeria aged 50 years and above, that satisfied the criteria of the reference population. Ethical approval and informed consent were obtained. Venous blood was collected from reference individuals and serum 25(OH)D was determined by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. Data were analysed using a non-parametric, bootstrap method to obtain the central 95% reference limits and 90% confidence intervals of the lower and upper limits of the reference interval respectively.
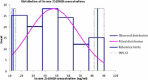
Results: One hundred and twenty-four (62 males and 62 females) participants were recruited. The median (25th -75th percentile) of serum 25(OH)D was 56 (35 - 71) ng/ml. The 2.5th percentile defined the lower reference limit and it was 21 ng/ml with 90% confidence interval (20 - 23) ng/ml; while the 97.5th percentile defined the upper reference limit and it was 93 ng/ml with 90% confidence interval (90 - 98) ng/ml.
Conclusion: The reference interval for serum 25(OH)D for the selected African elderly population in Enugu, Nigeria was determined to be 21 to 93 ng/ml.
Keywords: Bootstrap method; elderly; reference interval; vitamin D.
© 2022 Nnakenyi ID et al.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Associations of serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D with metabolic syndrome and its components in elderly men and women: the Korean Urban Rural Elderly cohort study.BMC Geriatr. 2019 Apr 11;19(1):102. doi: 10.1186/s12877-019-1118-y. BMC Geriatr. 2019. PMID: 30975093 Free PMC article.
-
Vitamin D status and predictors of hypovitaminosis D in Italian children and adolescents: a cross-sectional study.Eur J Pediatr. 2013 Dec;172(12):1607-17. doi: 10.1007/s00431-013-2119-z. Eur J Pediatr. 2013. PMID: 23959324
-
Parathyroid hormone reference ranges in healthy individuals classified by vitamin D status.J Endocrinol Invest. 2019 Nov;42(11):1353-1360. doi: 10.1007/s40618-019-01075-w. Epub 2019 Jul 4. J Endocrinol Invest. 2019. PMID: 31273631 Free PMC article.
-
Vitamin D "insufficiency" in adults. Beware of vague concepts with uncertain clinical relevance.Prescrire Int. 2013 Oct;22(142):245-8. Prescrire Int. 2013. PMID: 24298597 Review.
-
[Frontiers in vitamin D; basic research and clinical application. Vitamin D and falls].Clin Calcium. 2011 Nov;21(11):71-9. Clin Calcium. 2011. PMID: 22040823 Review. Japanese.
Cited by
-
Editorial: Non-communicable diseases; sexual reproductive issues; infectious diseases and health systems challenges.Afr Health Sci. 2022 Dec;22(4):i-v. doi: 10.4314/ahs.v22i4.1. Afr Health Sci. 2022. PMID: 37092096 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Hollis BW. Assessment of vitamin D nutritional and hormonal status: What to measure and how to do it. Calcified Tissue International. 1996;58(1):4–5. - PubMed
-
- Haddad JG, Jr, Hahn TJ. Natural and synthetic sources of circulating 25-hydroxyvitamin D in man. Nature. 1973;244:515–527. - PubMed
-
- Norman AW, Frankel JB, Heldt AM, Grodsky GM. Vitamin D deficiency inhibits pancreatic secretion of insulin. Science. 2001;209:823–825. - PubMed
-
- Vinh-Quoc-Luong K, Thi-Hoang-Nguyen L. Vitamin D and Parkinson's disease. J Neuroscien Res. 2012;90(12):2227–2236. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical