Mutations Status of NOTCH Signaling Pathway Predict Prognosis of Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors in Colorectal Cancer
- PMID: 37092128
- PMCID: PMC10120821
- DOI: 10.2147/JIR.S394894
Mutations Status of NOTCH Signaling Pathway Predict Prognosis of Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors in Colorectal Cancer
Abstract
Purpose: In recent years, tumour immunotherapy has ushered in a new era of oncology treatment. However, the use of immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs) in the treatment of CRC remains limited. There is an urgent clinical need for precise biomarkers that can aid in the screening and treatment of CRC subtypes. Therefore, we focused on the NOTCH pathway mutation status and conducted a systematic analysis for its predictive value of ICI therapy efficacy.
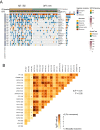
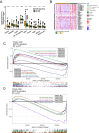
Methods: We collected mutational and clinical data from cohorts of CRC patients treated with ICIs. The relationship between NOTCH pathway mutations (NOTCH-MT) and CRC immunotherapy prognosis was analysed using univariate and multivariate Cox regression models. CRC cohort data from The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) database were combined to obtain a comprehensive overview of immunogenicity and tumour microenvironment (TME) differences among different NOTCH pathway mutation statuses.
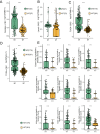
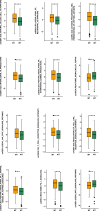
Results: We observed greater infiltration of M1 macrophages, CD8+ T cells, neutrophils, and activated natural killer (NK) cells with NOTCH-MT status. Immunogenicity was also significantly higher in patients with NOTCH-MT, as were tumour mutational burden (TMB), neoantigen load (NAL), and the number of mutations in DNA damage repair (DDR) pathways.
Conclusion: NOTCH-MT status was strongly associated with the prognosis of CRC patients treated with ICIs and is expected to serve as a novel biomarker and therapeutic target for CRC.
Keywords: CRC; ICIs; NOTCH; biomarker; tumour microenvironment.
© 2023 Lin et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures




References
-
- Tanzadehpanah H, Bahmani A, Hosseinpour Moghadam N, et al. Synthesis, anticancer activity, and β-lactoglobulin binding interactions of multitargeted kinase inhibitor sorafenib tosylate (SORt) using spectroscopic and molecular modelling approaches. Luminescence. 2021;36(1):117–128. doi:10.1002/bio.3929 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

