Design and statistical optimisation of emulsomal nanoparticles for improved anti-SARS-CoV-2 activity of N-(5-nitrothiazol-2-yl)-carboxamido candidates: in vitro and in silico studies
- PMID: 37092260
- PMCID: PMC10128464
- DOI: 10.1080/14756366.2023.2202357
Design and statistical optimisation of emulsomal nanoparticles for improved anti-SARS-CoV-2 activity of N-(5-nitrothiazol-2-yl)-carboxamido candidates: in vitro and in silico studies
Abstract
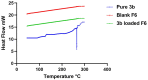
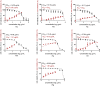
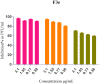
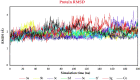
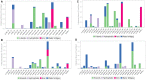
In this article, emulsomes (EMLs) were fabricated to encapsulate the N-(5-nitrothiazol-2-yl)-carboxamido derivatives (3a-3g) in an attempt to improve their biological availability and antiviral activity. Next, both cytotoxicity and anti-SARS-CoV-2 activities of the examined compounds loaded EMLs (F3a-g) were assessed in Vero E6 cells via MTT assay to calculate the CC50 and inhibitory concentration 50 (IC50) values. The most potent 3e-loaded EMLs (F3e) elicited a selectivity index of 18 with an IC50 value of 0.73 μg/mL. Moreover, F3e was selected for further elucidation of a possible mode of action where the results showed that it exhibited a combination of virucidal (>90%), viral adsorption (>80%), and viral replication (>60%) inhibition. Besides, molecular docking and MD simulations towards the SARS-CoV-2 Mpro were performed. Finally, a structure-activity relationship (SAR) study focussed on studying the influence of altering the size, type, and flexibility of the α-substituent to the carboxamide in addition to compound contraction on SARS-CoV-2 activity.HighlightsEmulsomes (EMLs) were fabricated to encapsulate the N-(5-nitrothiazol-2-yl)-carboxamido derivatives (3a-3g).The most potent 3e-loaded EMLs (F3e) showed an IC50 value of 0.73 μg/mL against SARS-CoV-2.F3e exhibited a combination of virucidal (>90%), viral adsorption (>80%), and viral replication (>60%) inhibition.Molecular docking, molecular dynamics (MD) simulations, and MM-GBSA calculations were performed.Structure-activity relationship (SAR) study was discussed to study the influence of altering the size, type, and flexibility of the α-substituent to the carboxamide on the anti-SARS-CoV-2 activity.
Keywords: N-(5-nitrothiazol-2-yl)-carboxamide; SAR; anti-SARS-CoV-2; emulsomes; mechanistic study.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest was reported by the author(s).
Figures






Similar articles
-
Ligand-based design, synthesis, computational insights, and in vitro studies of novel N-(5-Nitrothiazol-2-yl)-carboxamido derivatives as potent inhibitors of SARS-CoV-2 main protease.J Enzyme Inhib Med Chem. 2022 Dec;37(1):2112-2132. doi: 10.1080/14756366.2022.2105322. J Enzyme Inhib Med Chem. 2022. PMID: 35912578 Free PMC article.
-
Investigating the promising SARS-CoV-2 main protease inhibitory activity of secoiridoids isolated from Jasminum humile; in silico and in Vitro assessments with structure-activity relationship.J Biomol Struct Dyn. 2024 Aug;42(13):6941-6953. doi: 10.1080/07391102.2023.2240419. Epub 2023 Jul 28. J Biomol Struct Dyn. 2024. PMID: 37505066
-
Anticoagulants as Potential SARS-CoV-2 Mpro Inhibitors for COVID-19 Patients: In Vitro, Molecular Docking, Molecular Dynamics, DFT, and SAR Studies.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Oct 13;23(20):12235. doi: 10.3390/ijms232012235. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36293094 Free PMC article.
-
Antiviral evaluation of hydroxyethylamine analogs: Inhibitors of SARS-CoV-2 main protease (3CLpro), a virtual screening and simulation approach.Bioorg Med Chem. 2021 Oct 1;47:116393. doi: 10.1016/j.bmc.2021.116393. Epub 2021 Sep 4. Bioorg Med Chem. 2021. PMID: 34509862 Free PMC article.
-
Anti-SARS-CoV-2 activities of tanshinone IIA, carnosic acid, rosmarinic acid, salvianolic acid, baicalein, and glycyrrhetinic acid between computational and in vitro insights.RSC Adv. 2021 Sep 1;11(47):29267-29286. doi: 10.1039/d1ra05268c. eCollection 2021 Sep 1. RSC Adv. 2021. PMID: 35492070 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Identification of sulphonamide-tethered N-((triazol-4-yl)methyl)isatin derivatives as inhibitors of SARS-CoV-2 main protease.J Enzyme Inhib Med Chem. 2023 Dec;38(1):2234665. doi: 10.1080/14756366.2023.2234665. J Enzyme Inhib Med Chem. 2023. PMID: 37434404 Free PMC article.
-
Biological and computational assessments of thiazole derivative-reinforced bile salt enriched nano carriers: a new gate in targeting SARS-CoV-2 spike protein.RSC Adv. 2024 Dec 9;14(52):38778-38795. doi: 10.1039/d4ra07316a. eCollection 2024 Dec 3. RSC Adv. 2024. PMID: 39654925 Free PMC article.
-
Recent studies on protein kinase signaling inhibitors based on thiazoles: review to date.RSC Adv. 2024 Nov 19;14(50):36989-37018. doi: 10.1039/d4ra05601a. eCollection 2024 Nov 19. RSC Adv. 2024. PMID: 39569127 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Influence of the AgNPs Ligand on the Antiviral Activity Against HSV-2.Int J Nanomedicine. 2025 Mar 4;20:2659-2671. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S496050. eCollection 2025. Int J Nanomedicine. 2025. PMID: 40061878 Free PMC article.
-
Metabolites profiling, in-vitro and molecular docking studies of five legume seeds for Alzheimer's disease.Sci Rep. 2024 Aug 23;14(1):19637. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-68743-7. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39179586 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
