Epigenetic modulations in cancer: predictive biomarkers and potential targets for overcoming the resistance to topoisomerase I inhibitors
- PMID: 37092854
- PMCID: PMC10128461
- DOI: 10.1080/07853890.2023.2203946
Epigenetic modulations in cancer: predictive biomarkers and potential targets for overcoming the resistance to topoisomerase I inhibitors
Abstract
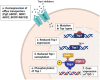
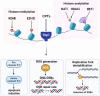
Introduction: Altered epigenetic map is frequently observed in cancer and recent investigations have demonstrated a pertinent role of epigenetic modifications in the response to many anticancer drugs including the DNA damaging agents. Topoisomerase I (Top I) is a well-known nuclear enzyme that is critical for DNA function and cell survival and its inhibition causes DNA strand breaks and cell cycle arrest. Inhibitors of human Top I have proven to be a prosperous chemotherapeutic treatment for a vast number of cancer patients. While the treatment is efficacious in many cases, resistance and altered cellular response remain major therapeutic issues.
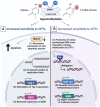
Areas covered: This review highlights the evidence available till date on the influence of different epigenetic modifications on the response to Top I inhibitors as well as the implications of targeting epigenetic alterations for improving the efficacy and safety of Top I inhibitors.
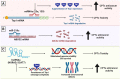
Expert opinion: The field of epigenetic research is steadily growing. With its assistance, we could gain better understanding on how drug response and resistance work. Epigenetics can evolve as possible biomarkers and predictors of response to many medications including Top I inhibitors, and could have significant clinical implications that necessitate deeper attention.HIGHLIGHTSEpigenetic alterations, including DNA methylation and histone modifications, play a pertinent role in the response to several anticancer treatments, including DNA damaging agents like Top I inhibitors.Although camptothecin derivatives are used clinically as Top I inhibitors for management of cancer, certain types of cancer have inherent and or acquired resistance that limit the curative potential of them.Epigenetic modifications like DNA hypomethylation can either increase or decrease sensitivity to Top I inhibitors by different mechanisms.The combination of Top I inhibitors with the inhibitors of histone modifying enzymes can result in enhanced cytotoxic effects and sensitization of resistant cells to Top I inhibitors.MicroRNAs were found to directly influence the expression of Top I and other proteins in cancer cells resulting in positive or negative alteration of the response to Top I inhibitors.lncRNAs and their genetic polymorphisms have been found to be associated with Top I function and the response to its inhibitors.Clinical trials of epigenetic drugs in combination with Top I inhibitors are plentiful and some of them showed potentially promising outcomes.
Keywords: Cancer; DNA methylation; Top I; Top I inhibitors; epigenetic; histone modifications; noncoding RNAs; resistance.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no relevant affiliations or financial involvement with any organization or entity with a financial interest in or financial conflict with the subject matter or materials discussed in the manuscript.
Figures
Similar articles
-
DNA repair and resistance to topoisomerase I inhibitors: mechanisms, biomarkers and therapeutic targets.Curr Med Chem. 2012;19(23):3874-85. doi: 10.2174/092986712802002590. Curr Med Chem. 2012. PMID: 22788763 Review.
-
Role of epigenetic drugs in sensitizing cancers to anticancer therapies: emerging trends and clinical advancements.Epigenomics. 2023 Apr;15(8):517-537. doi: 10.2217/epi-2023-0142. Epub 2023 Jun 14. Epigenomics. 2023. PMID: 37313832 Review.
-
An Update of Epigenetic Drugs for the Treatment of Cancers and Brain Diseases: A Comprehensive Review.Genes (Basel). 2023 Apr 6;14(4):873. doi: 10.3390/genes14040873. Genes (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37107631 Free PMC article. Review.
-
DNA methylation and microRNA biomarkers for noninvasive detection of gastric and colorectal cancer.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2014 Dec 5;455(1-2):43-57. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2014.08.001. Epub 2014 Aug 13. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2014. PMID: 25128828 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Epigenetic therapy in non-small-cell lung cancer: targeting DNA methyltransferases and histone deacetylases.Expert Opin Biol Ther. 2013 Sep;13(9):1273-85. doi: 10.1517/14712598.2013.819337. Epub 2013 Jul 17. Expert Opin Biol Ther. 2013. PMID: 23859704 Review.
Cited by
-
Understanding Cancer's Defense against Topoisomerase-Active Drugs: A Comprehensive Review.Cancers (Basel). 2024 Feb 6;16(4):680. doi: 10.3390/cancers16040680. Cancers (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38398072 Free PMC article. Review.
-
miRNA-Based Technologies in Cancer Therapy.J Pers Med. 2023 Nov 9;13(11):1586. doi: 10.3390/jpm13111586. J Pers Med. 2023. PMID: 38003902 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Development and validation of a generic methyltransferase enzymatic assay based on an SAH riboswitch.SLAS Discov. 2024 Jun;29(4):100161. doi: 10.1016/j.slasd.2024.100161. Epub 2024 May 22. SLAS Discov. 2024. PMID: 38788976 Free PMC article.
-
Pharmacoepigenetic Biomarkers in Inflammatory Bowel Diseases: A Narrative Review.Yale J Biol Med. 2025 Jun 30;98(2):171-186. doi: 10.59249/FTXB7704. eCollection 2025 Jun. Yale J Biol Med. 2025. PMID: 40589936 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Multidrug Resistance: Are We Still Afraid of the Big Bad Wolf.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2025 Jun 14;18(6):895. doi: 10.3390/ph18060895. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40573290 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Mognato M, Burdak-Rothkamm S, Rothkamm K.. Interplay between DNA replication stress, chromatin dynamics and DNA-damage response for the maintenance of genome stability. Mutat Res Rev Mutat Res. 2021;787:1. - PubMed
-
- Das J, Chandra L, Gandhi G, et al. . Evaluation of promoter hypermethylation of tumor suppressor gene BRCA1 in epithelial ovarian cancer. J Cancer Res Ther. 2022;18(6):1578–1582. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
