p38 MAPK activation and STIM1-Orai3 association mediate TRPC6 externalization
- PMID: 37093037
- PMCID: PMC10228675
- DOI: 10.1152/ajpcell.00425.2022
p38 MAPK activation and STIM1-Orai3 association mediate TRPC6 externalization
Abstract
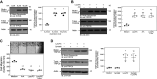
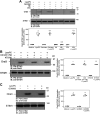
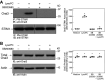
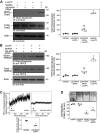
Endothelial cell (EC) migration is critical for the repair of monolayer disruption following angioplasties, but migration is inhibited by lipid oxidation products, including lysophosphatidylcholine (lysoPC), which open canonical transient receptor potential 6 (TRPC6) channels. TRPC6 activation requires an increase in intracellular Ca2+ concentration ([Ca2+]i), the source of which is unknown. LysoPC can activate phospholipase A2 to release arachidonic acid (ArA). ArA can activate arachidonic acid-regulated calcium (ARC) channels that are formed by stromal interaction molecule 1 (STIM1) and Orai1 and Orai3 proteins. Both lysoPC and ArA can activate p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) that induces the phosphorylation required for STIM1-Orai3 association. This is accompanied by an increase in [Ca2+]i and TRPC6 externalization. The effect of lysoPC and ArA is not additive, suggesting activation of the same pathway. The increase in [Ca2+]i activates an Src kinase that leads to TRPC6 activation. Downregulation of Orai3 using siRNA blocks the lysoPC- or ArA-induced increase in [Ca2+]i and TRPC6 externalization and preserves EC migration. These data show that lysoPC induces activation of p38 MAPK, which leads to STIM1-Orai3 association and increased [Ca2+]i. This increase in [Ca2+]i activates an Src kinase leading to TRPC6 externalization, which initiates a cascade of events ending in cytoskeletal changes that disrupt EC migration. Blocking this pathway preserves EC migration in the presence of lipid oxidation products.NEW & NOTEWORTHY The major lysophospholipid component in oxidized LDL, lysophosphatidylcholine (lysoPC), can activate p38 MAP kinase, which in turn promotes externalization of Orai3 and STIM1-Orai3 association, suggesting involvement of arachidonic acid-regulated calcium (ARC) channels. The subsequent increase in intracellular calcium activates an Src kinase required for TRPC6 externalization. TRPC6 activation, which has been shown to inhibit endothelial cell migration, is blocked by p38 MAP kinase or Orai3 downregulation, and this partially preserves endothelial migration in lysoPC.
Keywords: TRPC6; arachidonic acid; calcium; endothelial; migration.
Conflict of interest statement
No conflicts of interest, financial or otherwise, are declared by the authors.
Figures







Similar articles
-
Activation of the cytosolic calcium-independent phospholipase A2 β isoform contributes to TRPC6 externalization via release of arachidonic acid.J Biol Chem. 2021 Oct;297(4):101180. doi: 10.1016/j.jbc.2021.101180. Epub 2021 Sep 10. J Biol Chem. 2021. PMID: 34509476 Free PMC article.
-
iPLA2 inhibition blocks LysoPC-induced TRPC6 externalization and promotes Re-endothelialization of carotid injuries in hypercholesterolemic mice.Cell Calcium. 2023 Jun;112:102734. doi: 10.1016/j.ceca.2023.102734. Epub 2023 Apr 5. Cell Calcium. 2023. PMID: 37030190 Free PMC article.
-
Membrane translocation of TRPC6 channels and endothelial migration are regulated by calmodulin and PI3 kinase activation.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2016 Feb 23;113(8):2110-5. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1600371113. Epub 2016 Feb 8. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2016. PMID: 26858457 Free PMC article.
-
Orai3: Oncochannel with therapeutic potential.Cell Calcium. 2020 Sep;90:102247. doi: 10.1016/j.ceca.2020.102247. Epub 2020 Jun 26. Cell Calcium. 2020. PMID: 32659517 Review.
-
Arachidonic acid, ARC channels, and Orai proteins.Cell Calcium. 2009 Jun;45(6):602-10. doi: 10.1016/j.ceca.2009.02.001. Epub 2009 Mar 17. Cell Calcium. 2009. PMID: 19278724 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Nrf2 pathway activation promotes the expression of genes related to glutathione metabolism in alcohol-exposed astrocytes.PeerJ. 2024 May 31;12:e17541. doi: 10.7717/peerj.17541. eCollection 2024. PeerJ. 2024. PMID: 38832034 Free PMC article.
-
A Putative Role for TRPC6 in Immune-Mediated Kidney Injury.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Nov 16;24(22):16419. doi: 10.3390/ijms242216419. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 38003608 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Updated insights on ASK1 signaling: mechanisms, regulation, and therapeutic potential in diseases.Mol Cell Biochem. 2025 Jun 14. doi: 10.1007/s11010-025-05330-y. Online ahead of print. Mol Cell Biochem. 2025. PMID: 40515958 Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

