A Phase I/II Trial of HER2 Vaccine-Primed Autologous T-Cell Infusions in Patients with Treatment Refractory HER2-Overexpressing Breast Cancer
- PMID: 37093223
- PMCID: PMC10754340
- DOI: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-22-3578
A Phase I/II Trial of HER2 Vaccine-Primed Autologous T-Cell Infusions in Patients with Treatment Refractory HER2-Overexpressing Breast Cancer
Abstract
Purpose: High levels of type I T cells are needed for tumor eradication. We evaluated whether the HER2-specific vaccine-primed T cells are readily expanded ex vivo to achieve levels needed for therapeutic infusion.
Patients and methods: Phase I/II nonrandomized trial of escalating doses of ex vivo-expanded HER2-specific T cells after in vivo priming with a multiple peptide-based HER2 intracellular domain (ICD) vaccine. Vaccines were given weekly for a total of three immunizations. Two weeks after the third vaccine, patients underwent leukapheresis for T-cell expansion, then received three escalating cell doses over 7- to 10-day intervals. Booster vaccines were administered after the T-cell infusions. The primary objective was safety. The secondary objectives included extent and persistence of HER2-specific T cells, development of epitope spreading, and clinical response. Patients received a CT scan prior to enrollment and 1 month after the last T-cell infusion.
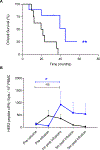
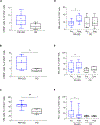
Results: Nineteen patients received T-cell infusions. Treatment was well tolerated. One month after the last T-cell infusion, 82% of patients had significantly augmented T cells to at least one of the immunizing epitopes and 81% of patients demonstrated enhanced intramolecular epitope spreading compared with baseline (P < 0.05). There were no complete responses, one partial response (6%), and eight patients with stable disease (47%), for a disease control rate of 53%. The median survival for those with progressive disease was 20.5 months and for responders (PR+SD) was 45.0 months.
Conclusions: Adoptive transfer of HER2 vaccine-primed T cells was feasible, was associated with minimal toxicity, and resulted in an increased overall survival in responding patients. See related commentary by Crosby et al., p. 3256.
©2023 American Association for Cancer Research.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interests: No disclosures were reported by the other authors.
Figures


Comment in
-
Beyond Neoantigens: Antigens Derived from Tumor Drivers as Cancer Vaccine Targets.Clin Cancer Res. 2023 Sep 1;29(17):3256-3258. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-23-1244. Clin Cancer Res. 2023. PMID: 37428103 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Fridman WH, Pages F, Sautes-Fridman C, Galon J. The immune contexture in human tumours: impact on clinical outcome. Nat Rev Cancer. 2012;12(4):298–306. - PubMed
-
- Datta J, Fracol M, McMillan MT, Berk E, Xu S, Goodman N, et al. Association of Depressed Anti-HER2 T-Helper Type 1 Response With Recurrence in Patients With Completely Treated HER2-Positive Breast Cancer: Role for Immune Monitoring. JAMA Oncol. 2016;2(2):242–6. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

