Hearing loss and COVID-19: an umbrella review
- PMID: 37093291
- PMCID: PMC10123565
- DOI: 10.1007/s00405-023-07982-2
Hearing loss and COVID-19: an umbrella review
Abstract
Introduction: COVID-19 can result in an extensive range of extrapulmonary, and neurological signs and symptoms such as olfactory and/or taste dysfunction, and otologic symptoms. The aim of this study was to investigate the hearing loss manifestation from COVID-19.
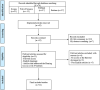
Methods: The goal of this umbrella review was to examine hearing loss associated with COVID-19 disease. English literature published until October 15, 2022 in online databases including PubMed, Scopus, Web of Science, and Embase was considered for this purpose. Eligibility of the articles for subsequent data extraction was evaluated in a two-step selection process with consideration to an inclusion/exclusion criterion. This review followed the PRISMA protocol and the Amstar-2 checklist for quality assessment.
Results: A total of four treatment strategies were used by different studies which included oral corticosteroids, intratympanic corticosteroids, combined oral and intratympanic corticosteroids, and hyperbaric oxygen therapy. Five studies investigated corticosteroid use in the forms of oral or intratympanic injection; four studies reported (complete or partial) hearing improvements after steroid treatment, while one study stated no significant improvement in hearing function. One study reported that oral corticosteroid monotherapy alone was not effective, while vestibular symptoms were ameliorated by a combination of oral prednisone, intratympanic dexamethasone injection, and hydroxychloroquine.
Conclusion: The findings suggest that despite being one of the rare complications of COVID-19, hearing loss can impact a patient's quality of life. The most common type reported was sensorineural hearing loss, which can be diagnosed with variable techniques.
Keywords: Auditory defect; COVID-19; Hearing damage; Hearing defect; Hearing loss; SARS-CoV-2.
© 2023. The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Springer-Verlag GmbH Germany, part of Springer Nature.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest regarding the publication of this manuscript.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Efficacy of high dose systemic versus combined (systemic and intratympanic) corticosteroid therapy in idiopathic sudden sensorineural hearing loss: A prospective randomized trial and risk factor analysis.Am J Otolaryngol. 2024 Jan-Feb;45(1):104099. doi: 10.1016/j.amjoto.2023.104099. Epub 2023 Nov 4. Am J Otolaryngol. 2024. PMID: 37948820 Clinical Trial.
-
Efficacy of Intratympanic Glucocorticoid Steroid Administration Therapy as an Initial Treatment for Idiopathic Sudden Sensorineural Hearing Loss During the COVID-19 Pandemic.Ear Nose Throat J. 2023 Dec;102(12):772-779. doi: 10.1177/01455613211032534. Epub 2021 Jul 12. Ear Nose Throat J. 2023. PMID: 34247535
-
Efficacy of systemic and intratympanic corticosteroid combination therapy versus intratympanic or systemic therapy in patients with idiopathic sudden sensorineural hearing loss: a randomized controlled trial.Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2018 Jan;275(1):89-97. doi: 10.1007/s00405-017-4808-0. Epub 2017 Nov 17. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2018. PMID: 29149379 Clinical Trial.
-
The effectiveness of intratympanic steroid injection in addition to systemic corticosteroids in the treatment of idiopathic sudden sensorineural hearing loss.Am J Otolaryngol. 2023 Jul-Aug;44(4):103872. doi: 10.1016/j.amjoto.2023.103872. Epub 2023 Apr 10. Am J Otolaryngol. 2023. PMID: 37060782 Review.
-
Intratympanic vs Systemic Corticosteroids in First-line Treatment of Idiopathic Sudden Sensorineural Hearing Loss: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis.JAMA Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2020 May 1;146(5):421-428. doi: 10.1001/jamaoto.2020.0047. JAMA Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2020. PMID: 32163109 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Association of COVID-19 infection and COVID-19 vaccination with idiopathic sudden sensorineural hearing loss in Malaysia: a case-control study.BMC Public Health. 2025 Mar 7;25(1):920. doi: 10.1186/s12889-025-21765-w. BMC Public Health. 2025. PMID: 40055620 Free PMC article.
-
The long-term Effects of the Coronavirus Disease (COVID-19) on Auditory Thresholds: A Case-Control Study.Iran J Otorhinolaryngol. 2025;37(2):85-86. doi: 10.22038/ijorl.2024.80236.3698. Iran J Otorhinolaryngol. 2025. PMID: 40162374 Free PMC article.
-
Idiopathic sudden sensorineural hearing loss after COVID-19 vaccination: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2024 Dec;281(12):6275-6281. doi: 10.1007/s00405-024-08839-y. Epub 2024 Jul 16. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2024. PMID: 39012479
-
Cochlear Implantation in Patients with Bilateral Sudden Sensorineural Hearing Loss after COVID-19 Infection.J Pers Med. 2023 Dec 14;13(12):1708. doi: 10.3390/jpm13121708. J Pers Med. 2023. PMID: 38138935 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Mehraeen E, Oliaei S, SeyedAlinaghi S, Karimi A, Mirzapour P, Afsahi AM, et al (2022) COVID-19 in pediatrics: a systematic review of current knowledge and practice. Infect Dis Drug Targ (Formerly Curr Drug Targ Infect Dis) 22(5):47–57 - PubMed
-
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) (2022) Symptoms of COVID-19. Available at: https://www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-ncov/symptoms-testing/symptoms.html
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous