Are there placebo or nocebo effects in balancing performance?
- PMID: 37093367
- PMCID: PMC10126169
- DOI: 10.1186/s41235-023-00476-z
Are there placebo or nocebo effects in balancing performance?
Abstract
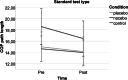
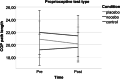
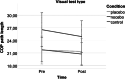
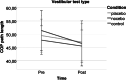
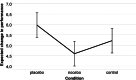
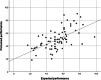
Placebo and nocebo effects could influence the perceived, actual, or both postural stabilities. Therefore, this experiment examined whether postural stability is susceptible to placebo and nocebo effects. Driven by expectations, these cognitions could influence the motor stability of people in physical rehabilitation and those with motion instability. We randomly assigned 78 participants to a placebo, nocebo, or control group. Then, we applied a sham sports cream with positive, negative, or neutral instructions about its impact on balance. Next, we tested postural stability with a modified version of the Modified Clinical Test of Sensory Interaction in Balance, including standard, proprioceptive, visual, and vestibular tests before and after the intervention. Further, we measured expected and perceived performance with visual analog scales and assessed trait anxiety, change in state anxiety, optimism, holistic thinking, persistence, and cooperation with questionnaires. The intervention did not affect actual test performances; similarly, trait and state variables and expectations did not have an impact. Furthermore, the experimental manipulation and trait and state variables did not significantly affect perceived performance. However, the association between expectation and perceived performance was strong (ϱ = 0.627, p < 0.001). These findings suggest that postural stability is not susceptible to placebo and nocebo influences. Still, there is a dissociation between objective and subjective performance, showing that expectations impact perceived but not actual performance, which could fuel motivation in rehabilitation settings.
Keywords: Balance; Expectations; Nocebo; Placebo; Postural stability.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Placebo and nocebo interventions impact perceived but not actual proprioceptive accuracy.PLoS One. 2024 Aug 30;19(8):e0307072. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0307072. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 39213316 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
A comparison of placebo and nocebo effects on objective and subjective postural stability: a double-edged sword?Front Hum Neurosci. 2022 Aug 18;16:967722. doi: 10.3389/fnhum.2022.967722. eCollection 2022. Front Hum Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 36061498 Free PMC article.
-
Can placebo or nocebo pills improve or impair cognition performance?Hum Psychopharmacol. 2023 May;38(3):e2869. doi: 10.1002/hup.2869. Epub 2023 May 4. Hum Psychopharmacol. 2023. PMID: 37140377
-
[Placebo and nocebo effects on itch : Methodological and clinical implications].Hautarzt. 2018 Aug;69(8):626-630. doi: 10.1007/s00105-018-4211-9. Hautarzt. 2018. PMID: 29947820 Review. German.
-
Placebo and nocebo effects in itch and pain.Handb Exp Pharmacol. 2014;225:205-14. doi: 10.1007/978-3-662-44519-8_12. Handb Exp Pharmacol. 2014. PMID: 25304534 Review.
Cited by
-
Light-Weight Wearable Gyroscopic Actuators Can Modulate Balance Performance and Gait Characteristics: A Proof-of-Concept Study.Healthcare (Basel). 2023 Oct 27;11(21):2841. doi: 10.3390/healthcare11212841. Healthcare (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37957986 Free PMC article.
-
Placebo and Nocebo Effects on Sports and Exercise Performance: A Systematic Literature Review Update.Nutrients. 2024 Jun 21;16(13):1975. doi: 10.3390/nu16131975. Nutrients. 2024. PMID: 38999724 Free PMC article.
-
Placebo and nocebo interventions impact perceived but not actual proprioceptive accuracy.PLoS One. 2024 Aug 30;19(8):e0307072. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0307072. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 39213316 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
References
-
- Babulka P, Berkes T, Szemerszky R, Köteles F. No effects of rosemary and lavender essential oil and a placebo pill on sustained attention, alertness, and heart rate. Flavour and Fragrance Journal. 2017;32(4):305–311. doi: 10.1002/ffj.3392. - DOI
-
- Beedie C, Benedetti F, Barbiani D, Camerone E, Cohen E, Coleman D, Davis A, Elsworth-Edelsten C, Flowers E, Foad A, Harvey S, Hettinga F, Hurst P, Lane A, Lindheimer J, Raglin J, Roelands B, Schiphof-Godart L, Szabo A. Consensus statement on placebo effects in sports and exercise: The need for conceptual clarity, methodological rigour, and the elucidation of neurobiological mechanisms. European Journal of Sport Science. 2018;18(10):1383–1389. doi: 10.1080/17461391.2018.1496144. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Benedetti F. Placebo effects: Understanding the mechanisms in health and disease. Oxford University Press; 2009.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
