Dissecting Psychiatric Heterogeneity and Comorbidity with Core Region-Based Machine Learning
- PMID: 37093448
- PMCID: PMC10387015
- DOI: 10.1007/s12264-023-01057-2
Dissecting Psychiatric Heterogeneity and Comorbidity with Core Region-Based Machine Learning
Abstract
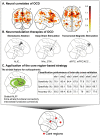
Machine learning approaches are increasingly being applied to neuroimaging data from patients with psychiatric disorders to extract brain-based features for diagnosis and prognosis. The goal of this review is to discuss recent practices for evaluating machine learning applications to obsessive-compulsive and related disorders and to advance a novel strategy of building machine learning models based on a set of core brain regions for better performance, interpretability, and generalizability. Specifically, we argue that a core set of co-altered brain regions (namely 'core regions') comprising areas central to the underlying psychopathology enables the efficient construction of a predictive model to identify distinct symptom dimensions/clusters in individual patients. Hypothesis-driven and data-driven approaches are further introduced showing how core regions are identified from the entire brain. We demonstrate a broadly applicable roadmap for leveraging this core set-based strategy to accelerate the pursuit of neuroimaging-based markers for diagnosis and prognosis in a variety of psychiatric disorders.
Keywords: Core region; Machine learning; Magnetic resonance imaging; Neuroimaging-based diagnosis; Obsessive-compulsive disorder; Psychiatric disorders.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Diagnostic Classification for Human Autism and Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder Based on Machine Learning From a Primate Genetic Model.Am J Psychiatry. 2021 Jan 1;178(1):65-76. doi: 10.1176/appi.ajp.2020.19101091. Epub 2020 Jun 16. Am J Psychiatry. 2021. PMID: 32539526
-
Diagnostic neuroimaging markers of obsessive-compulsive disorder: Initial evidence from structural and functional MRI studies.Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry. 2019 Apr 20;91:49-59. doi: 10.1016/j.pnpbp.2018.08.005. Epub 2018 Aug 11. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry. 2019. PMID: 30107192
-
Machine Learning With Neuroimaging: Evaluating Its Applications in Psychiatry.Biol Psychiatry Cogn Neurosci Neuroimaging. 2020 Aug;5(8):791-798. doi: 10.1016/j.bpsc.2019.11.007. Epub 2019 Nov 27. Biol Psychiatry Cogn Neurosci Neuroimaging. 2020. PMID: 31982357 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Prediction of Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder: Importance of Neurobiology-Aided Feature Design and Cross-Diagnosis Transfer Learning.Biol Psychiatry Cogn Neurosci Neuroimaging. 2022 Jul;7(7):735-746. doi: 10.1016/j.bpsc.2021.12.003. Epub 2021 Dec 18. Biol Psychiatry Cogn Neurosci Neuroimaging. 2022. PMID: 34929344
-
Predicting obsessive-compulsive disorder severity combining neuroimaging and machine learning methods.J Affect Disord. 2013 Sep 25;150(3):1213-6. doi: 10.1016/j.jad.2013.05.041. Epub 2013 Jun 14. J Affect Disord. 2013. PMID: 23769292
Cited by
-
A comprehensive review for machine learning on neuroimaging in obsessive-compulsive disorder.Front Hum Neurosci. 2023 Nov 1;17:1280512. doi: 10.3389/fnhum.2023.1280512. eCollection 2023. Front Hum Neurosci. 2023. PMID: 38021236 Free PMC article.
-
Artificial intelligence based advancements in nanomedicine for brain disorder management: an updated narrative review.Front Med (Lausanne). 2025 May 13;12:1599340. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2025.1599340. eCollection 2025. Front Med (Lausanne). 2025. PMID: 40432717 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

