Multi-channel deep learning model-based myocardial spatial-temporal morphology feature on cardiac MRI cine images diagnoses the cause of LVH
- PMID: 37093501
- PMCID: PMC10126185
- DOI: 10.1186/s13244-023-01401-0
Multi-channel deep learning model-based myocardial spatial-temporal morphology feature on cardiac MRI cine images diagnoses the cause of LVH
Abstract
Background: To develop a fully automatic framework for the diagnosis of cause for left ventricular hypertrophy (LVH) via cardiac cine images.
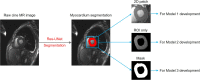
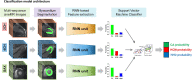
Methods: A total of 302 LVH patients with cine MRI images were recruited as the primary cohort. Another 53 LVH patients prospectively collected or from multi-centers were used as the external test dataset. Different models based on the cardiac regions (Model 1), segmented ventricle (Model 2) and ventricle mask (Model 3) were constructed. The diagnostic performance was accessed by the confusion matrix with respect to overall accuracy. The capability of the predictive models for binary classification of cardiac amyloidosis (CA), hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (HCM) or hypertensive heart disease (HHD) were also evaluated. Additionally, the diagnostic performance of best Model was compared with that of 7 radiologists/cardiologists.
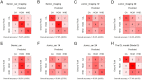
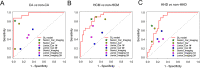
Results: Model 3 showed the best performance with an overall classification accuracy up to 77.4% in the external test datasets. On the subtasks for identifying CA, HCM or HHD only, Model 3 also achieved the best performance with AUCs yielding 0.895-0.980, 0.879-0.984 and 0.848-0.983 in the validation, internal test and external test datasets, respectively. The deep learning model showed non-inferior diagnostic capability to the cardiovascular imaging expert and outperformed other radiologists/cardiologists.
Conclusion: The combined model based on the mask of left ventricular segmented from multi-sequences cine MR images shows favorable and robust performance in diagnosing the cause of left ventricular hypertrophy, which could be served as a noninvasive tool and help clinical decision.
Keywords: Cardiac cine MRI; Case prediction; Deep learning; Left ventricular hypertrophy.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests. H-KY is an employee of Infervision Medical Technology Co., Ltd, Beijing, China.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Intelligent diagnosis of left ventricular hypertrophy using transthoracic echocardiography videos.Comput Methods Programs Biomed. 2022 Nov;226:107182. doi: 10.1016/j.cmpb.2022.107182. Epub 2022 Oct 12. Comput Methods Programs Biomed. 2022. PMID: 36257197
-
Myocardial contraction fraction derived from cardiovascular magnetic resonance cine images-reference values and performance in patients with heart failure and left ventricular hypertrophy.Eur Heart J Cardiovasc Imaging. 2017 Dec 1;18(12):1414-1422. doi: 10.1093/ehjci/jew324. Eur Heart J Cardiovasc Imaging. 2017. PMID: 28165128
-
A Deep Learning Approach to Classify Fabry Cardiomyopathy from Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy Using Cine Imaging on Cardiac Magnetic Resonance.Int J Biomed Imaging. 2024 Apr 26;2024:6114826. doi: 10.1155/2024/6114826. eCollection 2024. Int J Biomed Imaging. 2024. PMID: 38706878 Free PMC article.
-
Differential diagnosis of common etiologies of left ventricular hypertrophy using a hybrid CNN-LSTM model.Sci Rep. 2022 Dec 5;12(1):20998. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-25467-w. Sci Rep. 2022. PMID: 36470931 Free PMC article.
-
Using deep learning method to identify left ventricular hypertrophy on echocardiography.Int J Cardiovasc Imaging. 2022 Apr;38(4):759-769. doi: 10.1007/s10554-021-02461-3. Epub 2021 Nov 10. Int J Cardiovasc Imaging. 2022. PMID: 34757566 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Prospective Human Validation of Artificial Intelligence Interventions in Cardiology: A Scoping Review.JACC Adv. 2024 Aug 28;3(9):101202. doi: 10.1016/j.jacadv.2024.101202. eCollection 2024 Sep. JACC Adv. 2024. PMID: 39372457 Free PMC article.
References
Grants and funding
- 2022YFS0357/Key Research and Development Programs of Sichuan Province
- 22ZDYF1527)/Key Research and Development Programs of Sichuan Province
- 82200553/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 81600299/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 2021HXFH021/1.3.5 project for disciplines of excellence-Clinical Research Incubation Project, West China Hospital Sichuan University
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

