Depression and anxiety in people with cognitive impairment and dementia during the COVID-19 pandemic: Analysis of the English Longitudinal Study of Ageing
- PMID: 37093859
- PMCID: PMC10124844
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pmed.1004162
Depression and anxiety in people with cognitive impairment and dementia during the COVID-19 pandemic: Analysis of the English Longitudinal Study of Ageing
Abstract
Background: Some studies have identified declines in mental health during the Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic in different age groups, including older people. As anxiety and depression are common neuropsychiatric symptoms among people with cognitive impairment, the mental health experiences of older people during the pandemic should take cognitive function into consideration, along with assessments made prior to the pandemic. This study addresses evidence gaps to test whether changes in depression and anxiety among older people through the COVID-19 pandemic were associated with cognitive impairment. It also investigates whether associations varied according to key sources of sociodemographic inequality.
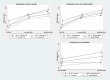
Methods and findings: Using data from the English Longitudinal Study of Ageing (ELSA) collected from 2018/2019 to November/December 2020, we estimated changes in depression and anxiety for people aged 50+ in England across 3 cognitive function groups: no impairment, mild cognitive impairment, and dementia. Conditional growth curve models were estimated for continuous measures over 3 time points (N = 5,286), with mixed-effects logistic regression used for binary measures. All models adjusted for demographics (age, gender, ethnicity, and cohabiting partnership), socioeconomics (education, wealth, and employment status), geography (urban/rural and English region), and health (self-rated and the presence of multimorbidity). We found that depression (measured with CES-D score) worsened from 2018/2019 to November/December 2020 for people with mild cognitive impairment (1.39 (95% CI: 1.29 to 1.49) to 2.16 (2.02 to 2.30)) or no impairment (1.17 (95%CI: 1.12 to 1.22) to 2.03 (1.96 to 2.10)). Anxiety, using a single-item rating of 0 to 10 also worsened among those with mild cognitive impairment (2.48 (2.30 to 2.66) to 3.14 (2.95 to 3.33)) or no impairment (2.20 (2.11 to 2.28) to 2.85 (2.77 to 2.95)). No statistically significant increases were found for those with dementia. Using a clinical cutoff for likely depression (CES-D ≥4), we found statistically significant increases in the probability of depression between 2018/2019 and November/December 2020 for those with no impairment (0.110 (0.099 to 0.120) to 0.206 (0.191 to 0.222)) and mild impairment (0.139 (0.120 to 0.159) to 0.234 (0.204 to 0.263)). We also found that differences according to cognitive function that existed before the pandemic were no longer present by June/July 2020, and there were no statistically significant differences in depression or anxiety among cognitive groups in November/December 2020. Wealth and education appeared to be stronger drivers for depression and anxiety, respectively, than cognitive impairment. For example, those with no impairment in the richest two-thirds scored 1.76 (1.69 to 1.82) for depression in June/July, compared to 2.01 (1.91 to 2.12) for those with no impairment in the poorest third and 2.03 (1.87 to 2.19) for those with impairment in the poorest third. Results may be limited by the small number of people with dementia and are generalizable only to people living in the community, not to those in institutional care settings.
Conclusions: Our findings suggest a convergence in mental health across cognitive function groups during the pandemic. This suggests mental health services will need to meet an increased demand from older adults, especially those not living with cognitive impairment. Further, with little significant change among those with dementia, their existing need for support will remain; policymakers and care practitioners should ensure this group continues to have equitable access to mental health support.
Copyright: © 2023 Beach et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Immediate and Longer-Term Changes in the Mental Health and Well-being of Older Adults in England During the COVID-19 Pandemic.JAMA Psychiatry. 2022 Feb 1;79(2):151-159. doi: 10.1001/jamapsychiatry.2021.3749. JAMA Psychiatry. 2022. PMID: 34935862 Free PMC article.
-
Associations of cognitive impairment with self-isolation and access to health and care during the COVID-19 pandemic in England.Sci Rep. 2023 Mar 28;13(1):5026. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-31241-3. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 36977759 Free PMC article.
-
Cognitive decline in older adults in the UK during and after the COVID-19 pandemic: a longitudinal analysis of PROTECT study data.Lancet Healthy Longev. 2023 Nov;4(11):e591-e599. doi: 10.1016/S2666-7568(23)00187-3. Lancet Healthy Longev. 2023. PMID: 37924840 Free PMC article.
-
[Neuropsychiatric symptoms in people living with dementia related to COVID-19 pandemic lockdown. Exploratory systematic review].Rev Neurol. 2022 Feb 1;74(3):83-92. doi: 10.33588/rn.7403.2021356. Rev Neurol. 2022. PMID: 35084733 Free PMC article. Spanish.
-
Diagnostic test accuracy of telehealth assessment for dementia and mild cognitive impairment.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Jul 20;7(7):CD013786. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013786.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021. PMID: 34282852 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Mental Health Impacts of COVID-19: Does Prepandemic Cognition and Dementia Status Matter?J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. 2024 Apr 1;79(4):glae028. doi: 10.1093/gerona/glae028. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. 2024. PMID: 38267562 Free PMC article.
-
A Selective Nuclear Factor-κB Inhibitor, JSH-23, Exhibits Antidepressant-like Effects and Reduces Brain Inflammation in Rats.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2024 Sep 26;17(10):1271. doi: 10.3390/ph17101271. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39458912 Free PMC article.
-
Accelerated brain ageing during the COVID-19 pandemic.Nat Commun. 2025 Jul 22;16(1):6411. doi: 10.1038/s41467-025-61033-4. Nat Commun. 2025. PMID: 40695794 Free PMC article.
-
Reimagining the journey to recovery: The COVID-19 pandemic and global mental health.PLoS Med. 2023 Apr 24;20(4):e1004224. doi: 10.1371/journal.pmed.1004224. eCollection 2023 Apr. PLoS Med. 2023. PMID: 37093801 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Salari N, Hosseinian-Far A, Jalali R, Vaisi-Raygani A, Rasoulpoor S, Mohammadi M, et al.. Prevalence of stress, anxiety, depression among the general population during the COVID-19 pandemic: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Global Health. 2020;16(1):57. doi: 10.1186/s12992-020-00589-w - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Santomauro DF, Mantilla Herrera AM, Shadid J, Zheng P, Ashbaugh C, Pigott DM, et al.. Global prevalence and burden of depressive and anxiety disorders in 204 countries and territories in 2020 due to the COVID-19 pandemic. Lancet. 2021;398(10312):1700–1712. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(21)02143-7 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

