GSK-3 at the heart of cardiometabolic diseases: Isoform-specific targeting is critical to therapeutic benefit
- PMID: 37094727
- PMCID: PMC10247467
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bbadis.2023.166724
GSK-3 at the heart of cardiometabolic diseases: Isoform-specific targeting is critical to therapeutic benefit
Abstract
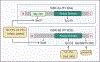
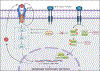
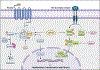
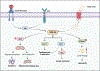
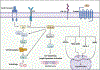
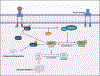
Glycogen synthase kinase-3 (GSK-3) is a family of serine/threonine kinases. The GSK-3 family has 2 isoforms, GSK-3α and GSK-3β. The GSK-3 isoforms have been shown to play overlapping as well as isoform-specific-unique roles in both, organ homeostasis and the pathogenesis of multiple diseases. In the present review, we will particularly focus on expanding the isoform-specific role of GSK-3 in the pathophysiology of cardiometabolic disorders. We will highlight recent data from our lab that demonstrated the critical role of cardiac fibroblast (CF) GSK-3α in promoting injury-induced myofibroblast transformation, adverse fibrotic remodeling, and deterioration of cardiac function. We will also discuss studies that found the exact opposite role of CF-GSK-3β in cardiac fibrosis. We will review emerging studies with inducible cardiomyocyte (CM)-specific as well as global isoform-specific GSK-3 KOs that demonstrated inhibition of both GSK-3 isoforms provides benefits against obesity-associated cardiometabolic pathologies. The underlying molecular interactions and crosstalk among GSK-3 and other signaling pathways will be discussed. We will briefly review the specificity and limitations of the available small molecule inhibitors targeting GSK-3 and their potential applications to treat metabolic disorders. Finally, we will summarize these findings and offer our perspective on envisioning GSK-3 as a therapeutic target for the management of cardiometabolic diseases.
Keywords: Cardiometabolic disease; Fibrosis; Glycogen synthase kinase; Heart failure; Hypertrophy; Myocardial infarction; Obesity.
Published by Elsevier B.V.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of competing interest All authors have read the journal's authorship statement and have reviewed and approved the manuscript. The authors have no conflicting interests to disclose in relation to this work.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Animal models of haploinsufficiency revealed the isoform-specific role of GSK-3 in HFD-induced obesity and glucose intolerance.Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2024 Dec 1;327(6):C1349-C1358. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00552.2024. Epub 2024 Sep 30. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2024. PMID: 39344416
-
Cardiac fibroblast GSK-3α aggravates ischemic cardiac injury by promoting fibrosis, inflammation, and impairing angiogenesis.Basic Res Cardiol. 2023 Sep 1;118(1):35. doi: 10.1007/s00395-023-01005-1. Basic Res Cardiol. 2023. PMID: 37656238 Free PMC article.
-
Fibroblast GSK-3α Promotes Fibrosis via RAF-MEK-ERK Pathway in the Injured Heart.Circ Res. 2022 Sep 16;131(7):620-636. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.122.321431. Epub 2022 Sep 2. Circ Res. 2022. PMID: 36052698 Free PMC article.
-
The GSK-3 family as therapeutic target for myocardial diseases.Circ Res. 2015 Jan 2;116(1):138-49. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.116.303613. Circ Res. 2015. PMID: 25552693 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Role of GSK-3 in Cardiac Health: Focusing on Cardiac Remodeling and Heart Failure.Curr Drug Targets. 2021;22(13):1568-1576. doi: 10.2174/1389450122666210224105430. Curr Drug Targets. 2021. PMID: 33655828 Review.
Cited by
-
Animal models of haploinsufficiency revealed the isoform-specific role of GSK-3 in HFD-induced obesity and glucose intolerance.Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2024 Dec 1;327(6):C1349-C1358. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00552.2024. Epub 2024 Sep 30. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2024. PMID: 39344416
-
Cardiac fibroblast GSK-3α aggravates ischemic cardiac injury by promoting fibrosis, inflammation, and impairing angiogenesis.Basic Res Cardiol. 2023 Sep 1;118(1):35. doi: 10.1007/s00395-023-01005-1. Basic Res Cardiol. 2023. PMID: 37656238 Free PMC article.
-
Xenon gas as a potential treatment for opioid use disorder, alcohol use disorder, and related disorders.Med Gas Res. 2025 Jun 1;15(2):234-253. doi: 10.4103/mgr.MEDGASRES-D-24-00063. Epub 2025 Jan 13. Med Gas Res. 2025. PMID: 39812023 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Embi N, Rylatt DB, Cohen P, Glycogen synthase kinase-3 from rabbit skeletal muscle. Separation from cyclic-AMP-dependent protein kinase and phosphorylase kinase, Eur J Biochem, 107 (1980) 519–527. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

