Isolation and Characterization of Pseudomonas aeruginosa Phages with a Broad Host Spectrum from Hospital Sewage Systems and Their Therapeutic Effect in a Mouse Model
- PMID: 37094788
- PMCID: PMC10540096
- DOI: 10.4269/ajtmh.22-0303
Isolation and Characterization of Pseudomonas aeruginosa Phages with a Broad Host Spectrum from Hospital Sewage Systems and Their Therapeutic Effect in a Mouse Model
Abstract
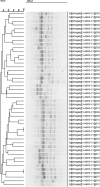
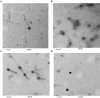
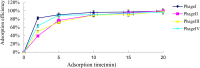
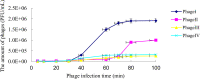
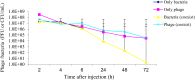
This study aimed to isolate and characterize phages as an alternative treatment of multidrug- or pan-drug-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Phage titers and bacterial densities correlated, with the phages disappearing after bacteria were eliminated. We isolated phages in filtered sewage water by a double-layered agar spot test. Fifty-eight P. aeruginosa strains were used to screen the host spectrum of the 14 phages isolated. Random amplification of polymorphic DNA-typing polymerase chain reaction was used to analyze the genomic homologies of the 58 host bacteria strains and four phages with a broad host spectrum. Transmission electron microscopy was used to observe the morphology of the four phages with a broad host spectrum. Mice with intraabdominal P. aeruginosa infection were used as an in vivo animal model to investigate the therapeutic effect of the selected phage. Four virulent phages with a broad host spectrum specific to P. aeruginosa strains were isolated. They were all double-stranded DNA viruses and belonged to four different genotypes. The test curve showed that phage I had the highest adsorption rate, the shortest latent period, and the largest burst size. The infected mouse model indicated that small doses of phage I could prevent the death of infected mice. Phage titers and bacterial densities correlated, with phages disappearing after bacteria were eliminated. Phage I was the most effective and promising treatment of drug-resistant P. aeruginosa.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Isolation and characterization of lytic bacteriophages from sewage at an egyptian tertiary care hospital against methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus clinical isolates.Saudi J Biol Sci. 2022 May;29(5):3097-3106. doi: 10.1016/j.sjbs.2022.03.019. Epub 2022 Mar 19. Saudi J Biol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35360502 Free PMC article.
-
Isolation and Characterization of Lytic Pseudomonas aeruginosa Bacteriophages Isolated from Sewage Samples from Tunisia.Viruses. 2022 Oct 25;14(11):2339. doi: 10.3390/v14112339. Viruses. 2022. PMID: 36366441 Free PMC article.
-
Isolation and Characterization of Three Pseudomonas aeruginosa Viruses with Therapeutic Potential.Microbiol Spectr. 2023 Jun 15;11(3):e0463622. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.04636-22. Epub 2023 May 1. Microbiol Spectr. 2023. PMID: 37125933 Free PMC article.
-
Bacteriophages of Pseudomonas aeruginosa: long-term prospects for use in phage therapy.Adv Virus Res. 2014;88:227-78. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-12-800098-4.00005-2. Adv Virus Res. 2014. PMID: 24373314 Review.
-
Challenges and Promises for Planning Future Clinical Research Into Bacteriophage Therapy Against Pseudomonas aeruginosa in Cystic Fibrosis. An Argumentative Review.Front Microbiol. 2018 May 4;9:775. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2018.00775. eCollection 2018. Front Microbiol. 2018. PMID: 29780361 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Isolation and characterization of a novel bacteriophage PUTH1 active against Pseudomonas aeruginosa.Virol J. 2025 Jul 19;22(1):248. doi: 10.1186/s12985-025-02859-8. Virol J. 2025. PMID: 40684166 Free PMC article.
-
Bacteriophage therapy to combat MDR non-fermenting Gram-negative bacteria causing nosocomial infections: recent progress and challenges.Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2025 Jun 6. doi: 10.1007/s00210-025-04345-y. Online ahead of print. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40478338 Review.
References
-
- Wilson R, Aksamit T, Aliberti S, De Soyza A, Elborn JS, Goeminne P, Hill AT, Menendez R, Polverino E, 2016. Challenges in managing Pseudomonas aeruginosa in non-cystic fibrosis bronchiectasis. Respir Med 117: 179–189. - PubMed
-
- Chen MJ, Wang H, 2003. Continuous surveillance of antimicrobial resistance among nosocomial gram-negative bacilli from intensive care units in China. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi 83: 375–381. - PubMed
-
- Sanford E, Farnaes L, Batalov S, Bainbridge M, Laubach S, Worthen HM, Tokita M, Kingsmore SF, Bradley J, 2018. Concomitant diagnosis of immune deficiency and Pseudomonas sepsis in a 19 month old with ecthyma gangrenosum by host whole-genome sequencing. Cold Spring Harb Mol Case Stud 4: a003244. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

