Preventive and therapeutic benefits of nelfinavir in rhesus macaques and human beings infected with SARS-CoV-2
- PMID: 37095086
- PMCID: PMC10123561
- DOI: 10.1038/s41392-023-01429-0
Preventive and therapeutic benefits of nelfinavir in rhesus macaques and human beings infected with SARS-CoV-2
Abstract
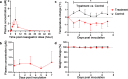
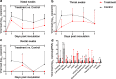
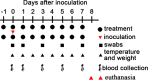
Effective drugs with broad spectrum safety profile to all people are highly expected to combat COVID-19 caused by SARS-CoV-2. Here we report that nelfinavir, an FDA approved drug for the treatment of HIV infection, is effective against SARS-CoV-2 and COVID-19. Preincubation of nelfinavir could inhibit the activity of the main protease of the SARS-CoV-2 (IC50 = 8.26 μM), while its antiviral activity in Vero E6 cells against a clinical isolate of SARS-CoV-2 was determined to be 2.93 μM (EC50). In comparison with vehicle-treated animals, rhesus macaque prophylactically treated with nelfinavir had significantly lower temperature and significantly reduced virus loads in the nasal and anal swabs of the animals. At necropsy, nelfinavir-treated animals had a significant reduction of the viral replication in the lungs by nearly three orders of magnitude. A prospective clinic study with 37 enrolled treatment-naive patients at Shanghai Public Health Clinical Center, which were randomized (1:1) to nelfinavir and control groups, showed that the nelfinavir treatment could shorten the duration of viral shedding by 5.5 days (9.0 vs. 14.5 days, P = 0.055) and the duration of fever time by 3.8 days (2.8 vs. 6.6 days, P = 0.014) in mild/moderate COVID-19 patients. The antiviral efficiency and clinical benefits in rhesus macaque model and in COVID-19 patients, together with its well-established good safety profile in almost all ages and during pregnancy, indicated that nelfinavir is a highly promising medication with the potential of preventative effect for the treatment of COVID-19.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- WHO. Coronavirus Disease (COVID-2019) Situation Reports. https://www.who.int/emergencies/diseases/novel-coronavirus-2019/situatio... (2023).
-
- Huang, T. et al. in Antiviral Drug Discovery and Development (eds Liu, X., Zhan, P., Menéndez-Arias, L. & Poongavanam, V.) 219–260 (Springer Singapore, 2021).
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

