CHST2-mediated sulfation of MECA79 antigens is critical for breast cancer cell migration and metastasis
- PMID: 37095090
- PMCID: PMC10126008
- DOI: 10.1038/s41419-023-05797-x
CHST2-mediated sulfation of MECA79 antigens is critical for breast cancer cell migration and metastasis
Abstract
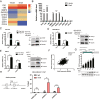
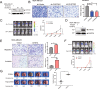
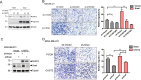
Snail is a denoted transcriptional repressor that plays key roles in epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) and metastasis. Lately, a plethora of genes can be induced by stable expression of Snail in multiple cell lines. However, the biological roles of these upregulated genes are largely elusive. Here, we report identification of a gene encoding the key GlcNAc sulfation enzyme CHST2 is induced by Snail in multiple breast cancer cells. Biologically, CHST2 depletion results in inhibition of breast cancer cell migration and metastasis, while overexpression of CHST2 promotes cell migration and lung metastasis in nude mice. In addition, the expression level of MECA79 antigen is elevated and blocking the cell surface MECA79 antigen with specific antibodies can override cell migration mediated by CHST2 upregulation. Moreover, the sulfation inhibitor sodium chlorate effectively inhibits the cell migration induced by CHST2. Collectively, these data provide novel insights into the biology of Snail/CHST2/MECA79 axis in breast cancer progression and metastasis as well as potential therapeutic strategy for the diagnosis and treatment of breast cancer metastasis.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Enhanced PAPSS2/VCAN sulfation axis is essential for Snail-mediated breast cancer cell migration and metastasis.Cell Death Differ. 2019 Mar;26(3):565-579. doi: 10.1038/s41418-018-0147-y. Epub 2018 Jun 28. Cell Death Differ. 2019. PMID: 29955124 Free PMC article.
-
microRNA-33a prevents epithelial-mesenchymal transition, invasion, and metastasis of gastric cancer cells through the Snail/Slug pathway.Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2019 Aug 1;317(2):G147-G160. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.00284.2018. Epub 2019 Apr 3. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2019. PMID: 30943047
-
Epidermal growth factor-like domain-containing protein 7 (EGFL7) enhances EGF receptor-AKT signaling, epithelial-mesenchymal transition, and metastasis of gastric cancer cells.PLoS One. 2014 Jun 19;9(6):e99922. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0099922. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 24945379 Free PMC article.
-
Snail/FOXK1/Cyr61 Signaling Axis Regulates the Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition and Metastasis in Colorectal Cancer.Cell Physiol Biochem. 2018;47(2):590-603. doi: 10.1159/000490015. Epub 2018 May 22. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2018. PMID: 29794466
-
Gemifloxacin inhibits migration and invasion and induces mesenchymal-epithelial transition in human breast adenocarcinoma cells.J Mol Med (Berl). 2014 Jan;92(1):53-64. doi: 10.1007/s00109-013-1083-4. Epub 2013 Sep 5. J Mol Med (Berl). 2014. PMID: 24005829
Cited by
-
Reassessing Breast Cancer-Associated Fibroblasts (CAFs) Interactions with Other Stromal Components and Clinico-Pathologic Parameters by Using Immunohistochemistry and Digital Image Analysis (DIA).Cancers (Basel). 2023 Jul 27;15(15):3823. doi: 10.3390/cancers15153823. Cancers (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37568639 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular mechanism underlying epithelial-mesenchymal transformation and cisplatin resistance in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma.Thorac Cancer. 2023 Nov;14(31):3069-3079. doi: 10.1111/1759-7714.15094. Epub 2023 Sep 17. Thorac Cancer. 2023. PMID: 37718469 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Sulfoconjugation of protein peptides and glycoproteins in physiology and diseases.Pharmacol Ther. 2023 Nov;251:108540. doi: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2023.108540. Epub 2023 Sep 28. Pharmacol Ther. 2023. PMID: 37777160 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Upregulation of Sulfated N-Glycans in Serum as Predictive Biomarkers for Early-Stage Breast Cancer.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 May 22;26(11):4968. doi: 10.3390/ijms26114968. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40507784 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

