Circulating cytokine levels in systemic sclerosis related interstitial lung disease and idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis
- PMID: 37095095
- PMCID: PMC10125994
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-023-31232-4
Circulating cytokine levels in systemic sclerosis related interstitial lung disease and idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis
Abstract
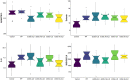
Exploration of cytokine levels in systemic sclerosis-associated interstitial lung disease (SSc-ILD) and idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF) is needed to find common and diverse biomolecular pathways. Circulating levels of 87 cytokines were compared amongst 19 healthy controls and consecutive patients with SSc-ILD (n = 39), SSc without ILD (n = 29), and IPF (n = 17) recruited from a Canadian centre using a log-linear model adjusted for age, sex, baseline forced vital capacity (FVC), and immunosuppressive or anti-fibrotic treatment at time of sampling. Also examined was annualized change in FVC. Four cytokines had Holm's corrected p-values less than 0.05. Eotaxin-1 levels were increased approximately two-fold in all patient categories compared to healthy controls. Interleukin-6 levels were eight-fold higher in all ILD categories compared to healthy controls. MIG/CXCL9 levels increased two-fold more in all but one patient category compared to healthy controls. Levels of a disintegrin and metalloproteinase with thrombospondin type 1 motif, member 13, (ADAMTS13) were lower for all categories of patients compared to controls. No substantial association was found for any of the cytokines with FVC change. Observed cytokine differences suggest both common and diverse pathways leading to pulmonary fibrosis. Further studies evaluating longitudinal change of these molecules would be informative.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
KK has received honoraria from Merck Canada Inc, Hoffman-La Roche Ltd., Pfizer Canada. MF is medical director of Mitogen Diagnostics Inc. and has received honoraria from diagnostic companies Werfen and Aesku. CR has received grants from Boehringer Ingelheim, Hoffmann-La Roche and consulting fees from Boehringer Ingelheim, Hoffmann-La Roche, Astra Zeneca, Veracyte, Ensho, Pliant Therapeutics. PW has received honoraria from Vertex, Valeo, and Boehringer Ingelheim. JVD has received consulting fees from Boehringer Ingelheim.
Figures
References
-
- Walker UA, Tyndall A, Czirjak L, Denton C, Farge-Bancel D, Kowal-Bielecka O, et al. Clinical risk assessment of organ manifestations in systemic sclerosis: a report from the EULAR Scleroderma Trials and Research group database. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2007;66(6):754–763. doi: 10.1136/ard.2006.062901. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- van den Hoogen F, Khanna D, Fransen J, Johnson SR, Baron M, Tyndall A, et al. 2013 classification criteria for systemic sclerosis: an American college of rheumatology/European league against rheumatism collaborative initiative. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2013;72(11):1747–1755. doi: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2013-204424. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials