Exogenous 24-epibrassinolide ameliorates tolerance to high-temperature by adjusting the biosynthesis of pigments, enzymatic, non-enzymatic antioxidants, and diosgenin content in fenugreek
- PMID: 37095206
- PMCID: PMC10125993
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-023-33913-6
Exogenous 24-epibrassinolide ameliorates tolerance to high-temperature by adjusting the biosynthesis of pigments, enzymatic, non-enzymatic antioxidants, and diosgenin content in fenugreek
Abstract
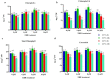
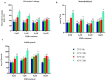
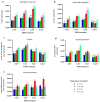
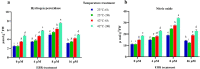
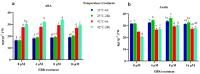
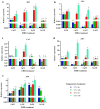
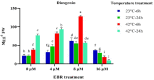
High-temperature stress is widely considered a main plant-growth-limiting factor. The positive effects of 24-epibrassinolide (EBR) as analogs of brassinosteroids (BRs) in modulating abiotic stresses have led this hormone to be referred to as a growth regulator in plants. The current study highlights the influence of EBR on enhancing tolerance to high-temperature and altering the diosgenin content in fenugreek. Different amounts of EBR (4, 8, and 16 μM), harvesting times (6, and 24 h), as well as temperature regimes (23 °C, and 42 °C) were, used as treatments. EBR application under normal temperature and high-temperature stress resulted in decreased malondialdehyde content and electrolyte leakage percentage, while the activity of antioxidant enzymes improved significantly. Exogenous EBR application possibly contributes to activating the nitric oxide, H2O2, and ABA-dependent pathways, enhancing the biosynthesis of abscisic acid and auxin, and regulating the signal transduction pathways, which raises fenugreek tolerance to high-temperature. The SQS (eightfold), SEP (2.8-fold), CAS (11-fold), SMT (17-fold), and SQS (sixfold) expression, considerably increased following EBR application (8 μM) compared to the control. Compared to the control, when the short-term (6 h) high-temperature stress was accompanied by EBR (8 μM), a sixfold increase in diosgenin content was achieved. Our findings highlight the potential role of exogenous 24-epibrassinolide in mitigating the high-temperature stress in fenugreek by stimulating the biosynthesis processes of enzymatic and non-enzymatic antioxidants, chlorophylls, and diosgenin. In conclusion, the current results could be of utmost importance in breeding or biotechnology-based programs of fenugreek and also in the researches related to the engineering of the biosynthesis pathway of diosgenin in this valuable plant.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Titanium dioxide -mediated regulation of enzymatic and non-enzymatic antioxidants, pigments, and diosgenin content promotes cold stress tolerance in Trigonella foenum-graecum L.Sci Rep. 2025 Jan 13;15(1):1837. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-84472-3. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 39805881 Free PMC article.
-
Melatonin confers fenugreek tolerance to salinity stress by stimulating the biosynthesis processes of enzymatic, non-enzymatic antioxidants, and diosgenin content.Front Plant Sci. 2022 Aug 8;13:890613. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2022.890613. eCollection 2022. Front Plant Sci. 2022. PMID: 36003823 Free PMC article.
-
The amelioration of salt stress-induced damage in fenugreek through the application of cold plasma and melatonin.Plant Physiol Biochem. 2024 Feb;207:108382. doi: 10.1016/j.plaphy.2024.108382. Epub 2024 Jan 21. Plant Physiol Biochem. 2024. PMID: 38271864
-
24-Epibrassinolide Ameliorates Endogenous Hormone Levels to Enhance Low-Temperature Stress Tolerance in Cucumber Seedlings.Int J Mol Sci. 2018 Aug 24;19(9):2497. doi: 10.3390/ijms19092497. Int J Mol Sci. 2018. PMID: 30149495 Free PMC article.
-
Abscisic acid is involved in brassinosteroids-induced chilling tolerance in the suspension cultured cells from Chorispora bungeana.J Plant Physiol. 2011 Jun 15;168(9):853-62. doi: 10.1016/j.jplph.2010.09.020. Epub 2011 Mar 27. J Plant Physiol. 2011. PMID: 21444124
Cited by
-
Synergistic effects of melatonin and 24-epibrassinolide on chickpea water deficit tolerance.BMC Plant Biol. 2024 Jul 15;24(1):671. doi: 10.1186/s12870-024-05380-2. BMC Plant Biol. 2024. PMID: 39004702 Free PMC article.
-
Differential responses of two fenugreek (Trigonella foenum-graecum L.) landraces pretreated with melatonin to prolonged drought stress and subsequent recovery.BMC Plant Biol. 2024 Mar 2;24(1):161. doi: 10.1186/s12870-024-04835-w. BMC Plant Biol. 2024. PMID: 38429697 Free PMC article.
-
Transcriptome Shock in Developing Embryos of a Brassica napus and Brassica rapa Hybrid.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Nov 12;24(22):16238. doi: 10.3390/ijms242216238. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 38003428 Free PMC article.
-
Titanium dioxide -mediated regulation of enzymatic and non-enzymatic antioxidants, pigments, and diosgenin content promotes cold stress tolerance in Trigonella foenum-graecum L.Sci Rep. 2025 Jan 13;15(1):1837. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-84472-3. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 39805881 Free PMC article.
-
Assessing the effects of 24-epibrassinolide and yeast extract at various levels on cowpea's morphophysiological and biochemical responses under water deficit stress.BMC Plant Biol. 2023 Nov 27;23(1):593. doi: 10.1186/s12870-023-04548-6. BMC Plant Biol. 2023. PMID: 38008746 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Acharya S, Srichamroen A, Basu S, Ooraikul B, Basu T. Improvement in the nutraceutical properties of fenugreek (Trigonella foenum-graecum L.) Songklanakarin J. Sci. Technol. 2006;28(1):1–9.
-
- Sadeghzadeh-Ahari D, Hass M, Kashi A, Amri A, Alizadeh K. Genetic variability of some agronomic traits in the Iranian fenugreek landraces under drought stress and non-stress conditions. Afr. J. Plant Sci. 2010;4(2):12–20.
-
- Meena S, Sastry E, Rajput S, Pandey Y. Stability of fenugreek (Trigonella foenum-graecum L.) genotypes for terminal heat and water stress. Legume Res. Int. J. 2015;38(5):589–597.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

