Exploring microstructure and petrophysical properties of microporous volcanic rocks through 3D multiscale and super-resolution imaging
- PMID: 37095281
- PMCID: PMC10126112
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-023-33687-x
Exploring microstructure and petrophysical properties of microporous volcanic rocks through 3D multiscale and super-resolution imaging
Abstract
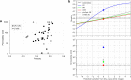
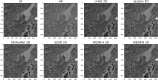
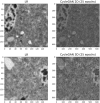
Digital rock physics offers powerful perspectives to investigate Earth materials in 3D and non-destructively. However, it has been poorly applied to microporous volcanic rocks due to their challenging microstructures, although they are studied for numerous volcanological, geothermal and engineering applications. Their rapid origin, in fact, leads to complex textures, where pores are dispersed in fine, heterogeneous and lithified matrices. We propose a framework to optimize their investigation and face innovative 3D/4D imaging challenges. A 3D multiscale study of a tuff was performed through X-ray microtomography and image-based simulations, finding that accurate characterizations of microstructure and petrophysical properties require high-resolution scans (≤ 4 μm/px). However, high-resolution imaging of large samples may need long times and hard X-rays, covering small rock volumes. To deal with these limitations, we implemented 2D/3D convolutional neural network and generative adversarial network-based super-resolution approaches. They can improve the quality of low-resolution scans, learning mapping functions from low-resolution to high-resolution images. This is one of the first efforts to apply deep learning-based super-resolution to unconventional non-sedimentary digital rocks and real scans. Our findings suggest that these approaches, and mainly 2D U-Net and pix2pix networks trained on paired data, can strongly facilitate high-resolution imaging of large microporous (volcanic) rocks.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures





References
-
- Allocca V, Colantuono P, Colella A, Piacentini SM, Piscopo V. Hydraulic properties of ignimbrites: Matrix and fracture permeabilities in two pyroclastic flow deposits from Cimino-Vico volcanoes (Italy) Bull. Eng. Geol. Environ. 2022;81:221. doi: 10.1007/s10064-022-02712-0. - DOI
-
- Bonamente E, Aquino A, Nicolini A, Cotana F. Experimental analysis and process modeling of carbon dioxide removal using tuff. Sustainability. 2016;8:1258. doi: 10.3390/su8121258. - DOI
-
- Heap MJ, Violay MES. The mechanical behaviour and failure modes of volcanic rocks: A review. Bull. Volcanol. 2021;83:33. doi: 10.1007/s00445-021-01447-2. - DOI
-
- Heiken, G. Tuffs-Their Properties, Uses, Hydrology and Resources. Geological Society of America (GSA) Special Paper, Vol. 408. 10.1130/SPE408 (2006).
-
- Rosi, M. & Sbrana, A. The Phlegrean Fields. CNR Quaderni de La Ricerca Scientifica 114 (1987).
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

