Prognostic factors after resection of locally advanced non-functional pancreatic neuroendocrine neoplasm: an analysis from the German Cancer Registry Group of the Society of German Tumor Centers
- PMID: 37095413
- PMCID: PMC10374814
- DOI: 10.1007/s00432-023-04785-0
Prognostic factors after resection of locally advanced non-functional pancreatic neuroendocrine neoplasm: an analysis from the German Cancer Registry Group of the Society of German Tumor Centers
Abstract
Objective: The available literature regarding outcome after pancreatic resection in locally advanced non-functional pNEN (LA-pNEN) is sparse. Therefore, this study evaluates the current survival outcomes and prognostic factors in after resection of LA-pNEN.
Materials and methods: This population-based analysis was derived from 17 German cancer registries from 2000 to 2019. Patients with upfront resected non-functional non-metastatic LA-pNEN were included.
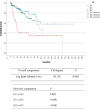
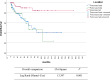
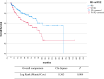
Results: Out of 2776 patients with pNEN, 277 met the inclusion criteria. 137 (45%) of the patients were female. The median age was 63 ± 18 years. Lymph node metastasis was present in 45%. G1, G2 and G3 pNEN were found in 39%, 47% and 14% of the patients, respectively. Resection of LA-pNEN resulted in favorable 3-, 5- and 10-year overall survival of 79%, 74%, and 47%. Positive resection margin was the only potentially modifiable independent prognostic factor for overall survival (HR 1.93, 95% CI 1.71-3.69, p value = 0.046), whereas tumor grade G3 (HR 5.26, 95% CI 2.09-13.25, p value < 0.001) and lymphangiosis (HR 2.35, 95% CI 1.20-4.59, p value = 0.012) were the only independent prognostic factors for disease-free survival.
Conclusion: Resection of LA-pNEN is feasible and associated with favorable overall survival. G1 LA-pNEN with negative resection margins and absence of lymph node metastasis and lymphangiosis might be considered as cured, while those not fulfilling these criteria might be considered as a high-risk group for disease progression. Herein, negative resection margins represent the only potentially modifiable prognostic factor in LA-pNEN but seem to be influenced by tumor grade.
Keywords: Pancreatic neuroendocrine neoplasms; Population-based analysis; Prognostic factors; Resection margin.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Impact of residual disease as a prognostic factor for survival in women with advanced epithelial ovarian cancer after primary surgery.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 Sep 26;9(9):CD015048. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD015048.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 36161421 Free PMC article.
-
Is the Thickness of the Margin Associated With Local Recurrence and Survival in Patients With Myxofibrosarcoma?Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2023 Nov 1;481(11):2125-2136. doi: 10.1097/CORR.0000000000002709. Epub 2023 May 29. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2023. PMID: 37249339 Free PMC article.
-
Are Current Survival Prediction Tools Useful When Treating Subsequent Skeletal-related Events From Bone Metastases?Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2024 Sep 1;482(9):1710-1721. doi: 10.1097/CORR.0000000000003030. Epub 2024 Mar 22. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2024. PMID: 38517402
-
Comparison of Two Modern Survival Prediction Tools, SORG-MLA and METSSS, in Patients With Symptomatic Long-bone Metastases Who Underwent Local Treatment With Surgery Followed by Radiotherapy and With Radiotherapy Alone.Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2024 Dec 1;482(12):2193-2208. doi: 10.1097/CORR.0000000000003185. Epub 2024 Jul 23. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2024. PMID: 39051924
-
Hysterectomy with radiotherapy or chemotherapy or both for women with locally advanced cervical cancer.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015 Apr 7;(4):CD010260. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD010260.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 Aug 22;8:CD010260. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD010260.pub3. PMID: 25847525 Updated.
Cited by
-
Multivisceral resection of nonfunctional pancreatic neuroendocrine neoplasm with nearby organ invasion: a case report.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023 Sep 26;14:1236685. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2023.1236685. eCollection 2023. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023. PMID: 37822595 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of dyslipidemia and lipid-lowering therapy with statins in patients with neuroendocrine tumors.J Neuroendocrinol. 2025 Feb;37(2):e13485. doi: 10.1111/jne.13485. Epub 2024 Dec 26. J Neuroendocrinol. 2025. PMID: 39726194 Free PMC article.
-
The extent of androgen receptor and HER2 expression allows for targeted therapy in most cases of salivary duct carcinoma: analysis of clinical and histopathological data in a tertiary care center.Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2024 Jul;281(7):3779-3789. doi: 10.1007/s00405-024-08627-8. Epub 2024 Apr 8. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2024. PMID: 38587651 Free PMC article.
-
[68/m-Satiety, increase in abdominal circumference, abdominal pain : Preparation for the medical specialist examination: part 45].Chirurgie (Heidelb). 2023 Sep;94(Suppl 1):81-84. doi: 10.1007/s00104-023-01888-9. Epub 2023 May 26. Chirurgie (Heidelb). 2023. PMID: 37237066 German. No abstract available.
-
When Should Lymphadenectomy Be Performed in Non-Metastatic Pancreatic Neuroendocrine Tumors? A Population-Based Analysis of the German Clinical Cancer Registry Group.Cancers (Basel). 2024 Jan 19;16(2):440. doi: 10.3390/cancers16020440. Cancers (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38275882 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Brierley JD, Gospodarowicz MK, Wittekind C (2017) TNM classification of malignant tumours. Wiley, New York
-
- Cong L, Liu Q, Zhang R, Cui M, Zhang X, Gao X, Guo J, Dai M, Zhang T, Liao Q, Zhao Y (2018) Tumor size classification of the 8(th) edition of TNM staging system is superior to that of the 7(th) edition in predicting the survival outcome of pancreatic cancer patients after radical resection and adjuvant chemotherapy. Sci Rep 8(1):10383 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Fusai GK, Tamburrino D, Partelli S, Lykoudis P, Pipan P, Di Salvo F, Beghdadi N, Dokmak S, Wiese D, Landoni L, Nessi C, Busch ORC, Napoli N, Jang JY, Kwon W, Del Chiaro M, Scandavini C, Abu-Awwad M, Armstrong T, Hilal MA, Allen PJ, Javed A, Kjellman M, Sauvanet A, Bartsch DK, Bassi C, van Dijkum E, Besselink MG, Boggi U, Kim SW, He J, Wolfgang CL, Falconi M (2021) Portal vein resection during pancreaticoduodenectomy for pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors. An international multicenter comparative study. Surgery 169(5):1093–1101 - PubMed
-
- Howe JR, Merchant NB, Conrad C, Keutgen XM, Hallet J, Drebin JA, Minter RM, Lairmore TC, Tseng JF, Zeh HJ, Libutti SK, Singh G, Lee JE, Hope TA, Kim MK, Menda Y, Halfdanarson TR, Chan JA, Pommier RF (2020) The North American Neuroendocrine Tumor Society consensus paper on the surgical management of pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors. Pancreas 49(1):1–33 - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

