Deleted in lymphocytic leukemia 2 (DLEU2): a possible biomarker that holds promise for future diagnosis and treatment of cancer
- PMID: 37095423
- PMCID: PMC10462543
- DOI: 10.1007/s12094-023-03149-x
Deleted in lymphocytic leukemia 2 (DLEU2): a possible biomarker that holds promise for future diagnosis and treatment of cancer
Abstract
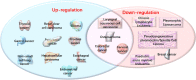
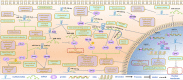
The mechanism of deleted in lymphocytic leukemia 2 (DLEU2)-long non-coding RNA in tumors has become a major point of interest in recent research related to the occurrence and development of a variety of tumors. Recent studies have shown that the long non-coding RNA DLEU2 (lncRNA-DLEU2) can cause abnormal gene or protein expression by acting on downstream targets in cancers. At present, most lncRNA-DLEU2 play the role of oncogenes in different tumors, which are mostly associated with tumor characteristics, such as proliferation, migration, invasion, and apoptosis. The data thus far show that because lncRNA-DLEU2 plays an important role in most tumors, targeting abnormal lncRNA-DLEU2 may be an effective treatment strategy for early diagnosis and improving the prognosis of patients. In this review, we integrated lncRNA-DLEU2 expression in tumors, its biological functions, molecular mechanisms, and the utility of DLEU2 as an effective diagnostic and prognostic marker of tumors. This study aimed to provide a potential direction for the diagnosis, prognosis, and treatment of tumors using lncRNA-DLEU2 as a biomarker and therapeutic target.
Keywords: Biomarker; Cancer; Functions; Molecular mechanisms; lncRNA-DLEU2.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
DLEU2: A Meaningful Long Noncoding RNA in Oncogenesis.Curr Pharm Des. 2021;27(20):2337-2343. doi: 10.2174/1381612826666201026150857. Curr Pharm Des. 2021. PMID: 33106136 Review.
-
Long noncoding RNA DLEU2 predicts a poor prognosis and enhances malignant properties in laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma through the miR-30c-5p/PIK3CD/Akt axis.Cell Death Dis. 2020 Jun 18;11(6):472. doi: 10.1038/s41419-020-2581-2. Cell Death Dis. 2020. PMID: 32555190 Free PMC article.
-
Long non-coding RNA DLEU2 promotes the progression of esophageal cancer through miR-30e-5p/E2F7 axis.Biomed Pharmacother. 2020 Mar;123:109650. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2019.109650. Epub 2019 Dec 26. Biomed Pharmacother. 2020. PMID: 31884338
-
LncRNA DLEU2 accelerates the tumorigenesis and invasion of non-small cell lung cancer by sponging miR-30a-5p.J Cell Mol Med. 2020 Jan;24(1):441-450. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.14749. Epub 2019 Nov 13. J Cell Mol Med. 2020. PMID: 31721438 Free PMC article.
-
Deleted in lymphocytic leukemia 2 (DLEU2): An lncRNA with dissimilar roles in different cancers.Biomed Pharmacother. 2021 Jan;133:111093. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2020.111093. Epub 2020 Dec 8. Biomed Pharmacother. 2021. PMID: 33378985 Review.
Cited by
-
DLEU2 facilitates bladder cancer progression through miR-103a-2-5p/SOS1 axis.PeerJ. 2025 Apr 8;13:e18995. doi: 10.7717/peerj.18995. eCollection 2025. PeerJ. 2025. PMID: 40226549 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- ZR2020MH320/Natural Science Foundation of Shandong Province
- 2019QL024/Academic promotion program of Shandong First Medical University
- 202019034/Jinan Clinical Medical Science and Technology Innovation Project
- YCZYPT(2022)-04-05/Multi center clinical application research of biological high-performance computing in precision medicine
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical