4-Octyl itaconate attenuates LPS-induced acute kidney injury by activating Nrf2 and inhibiting STAT3 signaling
- PMID: 37095432
- PMCID: PMC10127401
- DOI: 10.1186/s10020-023-00631-8
4-Octyl itaconate attenuates LPS-induced acute kidney injury by activating Nrf2 and inhibiting STAT3 signaling
Abstract
Background: Septic acute kidney injury (S-AKI) is the leading form of acute kidney failure among hospitalized patients, and the inflammatory response is involved in this process. 4-octyl itaconate (4-OI) is a multi-target itaconate derivative with potent anti-inflammatory action. However, it remains elusive whether and how 4-OI contributes to the regulation of S-AKI.
Methods: We employed a lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced AKI murine model and explored the potential renoprotective effect of 4-OI in vivo. In vitro experiments, BUMPT cells, a murine renal tubular cell line, were conducted to examine the effects of 4-OI on inflammation, oxidative stress, and mitophagy. Moreover, STAT3 plasmid was transfected in BUMPT cells to investigate the role of STAT3 signaling in the 4-OI-administrated state.
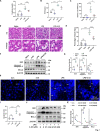
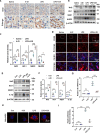
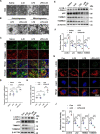
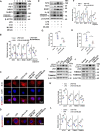
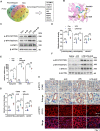
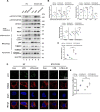
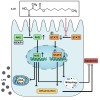
Results: We demonstrate that 4-OI protects against S-AKI through suppressing inflammation and oxidative stress and enhancing mitophagy. 4-OI significantly reduced the levels of Scr, BUN, Ngal as well as the tubular injury in LPS-induced AKI mice. 4-OI restrained inflammation by reducing macrophage infiltration and suppressing the expression of IL-1β and NLRP3 in the septic kidney. 4-OI also reduced ROS levels, as well as cleaved caspase-3 and boosted antioxidants such as HO-1, and NQO1 in mice. In addition, the 4-OI treatment significantly promoted mitophagy. Mechanistically, 4-OI activated Nrf2 signaling and suppressed phosphorylated STAT3 in vivo and vitro. Molecular docking revealed the binding affinity of 4-OI towards STAT3. ML385, a specific Nrf2 inhibitor, partially repressed the anti-inflammatory and anti-oxidative effects of 4-OI and partially restricted the mitophagy induced by 4-OI in vivo and in vitro. Transfected with STAT3 plasmid partially suppressed mitophagy and the anti-inflammatory effect provoked by 4-OI in vitro.
Conclusion: These data suggest that 4-OI ameliorates LPS-induced AKI by suppressing inflammation and oxidative stress and enhancing mitophagy through the overactivation of the Nrf2 signaling pathway, and inactivation of STAT3. Our study identifies 4-OI as a promising pharmacologic for S-AKI.
Keywords: 4-octyl itaconate; Acute kidney injury; Inflammation; Mitophagy; Nrf2; Oxidative stress; STAT3; sepsis.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Pharmacological inhibition of STING-mediated GPX4 autophagic degradation by 4-octyl itaconate ameliorates sepsis-induced acute kidney injury.Apoptosis. 2025 Jun;30(5-6):1410-1423. doi: 10.1007/s10495-025-02099-9. Epub 2025 Mar 22. Apoptosis. 2025. PMID: 40119983
-
Investigating the role of itaconate in macrophage activation and oxidative stress injury in sepsis-associated acute kidney injury.Mol Biol Rep. 2024 Apr 20;51(1):533. doi: 10.1007/s11033-024-09462-0. Mol Biol Rep. 2024. PMID: 38642169
-
4-Octyl itaconate alleviates endothelial cell inflammation and barrier dysfunction in LPS-induced sepsis via modulating TLR4/MAPK/NF-κB signaling : 4-Octyl itaconate alleviates endothelial dysfunction.Mol Med. 2025 Jun 16;31(1):240. doi: 10.1186/s10020-025-01160-2. Mol Med. 2025. PMID: 40524158 Free PMC article.
-
The anti-inflammatory effects of itaconate and its derivatives in neurological disorders.Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2024 Aug;78:37-49. doi: 10.1016/j.cytogfr.2024.07.001. Epub 2024 Jul 6. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2024. PMID: 38981775 Review.
-
Itaconate: A promising precursor for treatment of neuroinflammation associated depression.Biomed Pharmacother. 2023 Nov;167:115521. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2023.115521. Epub 2023 Sep 15. Biomed Pharmacother. 2023. PMID: 37717531 Review.
Cited by
-
4-Octyl itaconate attenuates renal tubular injury in db/db mice by activating Nrf2 and promoting PGC-1α-mediated mitochondrial biogenesis.Ren Fail. 2024 Dec;46(2):2403653. doi: 10.1080/0886022X.2024.2403653. Epub 2024 Sep 18. Ren Fail. 2024. PMID: 39291665 Free PMC article.
-
Integration of Network Pharmacology, Transcriptomics, and Metabolomics Strategies to Uncover the Mechanism of Chaihuang Qingfu Pill in Treating Sepsis-Induced Liver Injury.Drug Des Devel Ther. 2025 Jun 2;19:4665-4688. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S521626. eCollection 2025. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2025. PMID: 40486124 Free PMC article.
-
Pharmacological inhibition of STING-mediated GPX4 autophagic degradation by 4-octyl itaconate ameliorates sepsis-induced acute kidney injury.Apoptosis. 2025 Jun;30(5-6):1410-1423. doi: 10.1007/s10495-025-02099-9. Epub 2025 Mar 22. Apoptosis. 2025. PMID: 40119983
-
Regulation of metabolic microenvironment with a nanocomposite hydrogel for improved bone fracture healing.Bioact Mater. 2024 Apr 24;37:424-438. doi: 10.1016/j.bioactmat.2024.03.025. eCollection 2024 Jul. Bioact Mater. 2024. PMID: 38689661 Free PMC article.
-
Itaconate facilitates methane-induced Nrf2 pathway activation for mitigating liver ischemia and reperfusion injury.ILIVER. 2025 Feb 13;4(1):100144. doi: 10.1016/j.iliver.2025.100144. eCollection 2025 Mar. ILIVER. 2025. PMID: 40636783 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bagshaw SM, Uchino S, Bellomo R, Morimatsu H, Morgera S, Schetz M, Tan I, Bouman C, Macedo E, Gibney N, Tolwani A, van Oudemans HM, Ronco C, Kellum JA. Septic acute kidney injury in critically ill patients: clinical characteristics and outcomes. Clin J Am Soc Nephrology: CJASN. 2007;2(3):431–9. doi: 10.2215/cjn.03681106. - DOI - PubMed
-
- See EJ, Jayasinghe K, Glassford N, Bailey M, Johnson DW, Polkinghorne KR, Toussaint ND, Bellomo R. Long-term risk of adverse outcomes after acute kidney injury: a systematic review and meta-analysis of cohort studies using consensus definitions of exposure. Kidney Int. 2019;95(1):160–72. doi: 10.1016/j.kint.2018.08.036. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

