Model integrating CT-based radiomics and genomics for survival prediction in esophageal cancer patients receiving definitive chemoradiotherapy
- PMID: 37095586
- PMCID: PMC10127317
- DOI: 10.1186/s40364-023-00480-x
Model integrating CT-based radiomics and genomics for survival prediction in esophageal cancer patients receiving definitive chemoradiotherapy
Abstract
Background: Definitive chemoradiotherapy (dCRT) is a standard treatment option for locally advanced stage inoperable esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC). Evaluating clinical outcome prior to dCRT remains challenging. This study aimed to investigate the predictive power of computed tomography (CT)-based radiomics combined with genomics for the treatment efficacy of dCRT in ESCC patients.
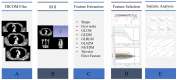
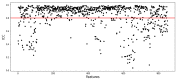
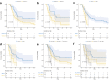
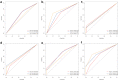
Methods: This retrospective study included 118 ESCC patients who received dCRT. These patients were randomly divided into training (n = 82) and validation (n = 36) groups. Radiomic features were derived from the region of the primary tumor on CT images. Least absolute shrinkage and selection operator (LASSO) regression was conducted to select optimal radiomic features, and Rad-score was calculated to predict progression-free survival (PFS) in training group. Genomic DNA was extracted from formalin-fixed and paraffin-embedded pre-treatment biopsy tissue. Univariate and multivariate Cox analyses were undertaken to identify predictors of survival for model development. The area under the receiver operating characteristic curve (AUC) and C-index were used to evaluate the predictive performance and discriminatory ability of the prediction models, respectively.
Results: The Rad-score was constructed from six radiomic features to predict PFS. Multivariate analysis demonstrated that the Rad-score and homologous recombination repair (HRR) pathway alterations were independent prognostic factors correlating with PFS. The C-index for the integrated model combining radiomics and genomics was better than that of the radiomics or genomics models in the training group (0.616 vs. 0.587 or 0.557) and the validation group (0.649 vs. 0.625 or 0.586).
Conclusion: The Rad-score and HRR pathway alterations could predict PFS after dCRT for patients with ESCC, with the combined radiomics and genomics model demonstrating the best predictive efficacy.
Keywords: Contrast-enhanced computed tomography; Esophageal squamous cell carcinoma; Genomics; Prognosis; Radiomics.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
CT-based radiomics combined with hematologic parameters for survival prediction in locally advanced esophageal cancer patients receiving definitive chemoradiotherapy.Insights Imaging. 2024 Mar 25;15(1):87. doi: 10.1186/s13244-024-01647-2. Insights Imaging. 2024. PMID: 38523188 Free PMC article.
-
Systemic immune-related spleen radiomics predict progression-free survival in patients with locally advanced cervical cancer underwent definitive chemoradiotherapy.BMC Med Imaging. 2024 Nov 15;24(1):310. doi: 10.1186/s12880-024-01492-1. BMC Med Imaging. 2024. PMID: 39548404 Free PMC article.
-
Development and validation of an [18F]FDG-PET/CT radiomic model for predicting progression-free survival for patients with stage II - III thoracic esophageal squamous cell carcinoma who are treated with definitive chemoradiotherapy.Acta Oncol. 2023 Feb;62(2):159-165. doi: 10.1080/0284186X.2023.2178859. Epub 2023 Feb 15. Acta Oncol. 2023. PMID: 36794365 Clinical Trial.
-
Current and future on definitive concurrent chemoradiotherapy for inoperable locally advanced esophageal squamous cell carcinoma.Front Oncol. 2024 Jan 26;14:1303068. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2024.1303068. eCollection 2024. Front Oncol. 2024. PMID: 38344202 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The prognostic value of radiogenomics using CT in patients with lung cancer: a systematic review.Insights Imaging. 2024 Oct 28;15(1):259. doi: 10.1186/s13244-024-01831-4. Insights Imaging. 2024. PMID: 39466334 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Computed tomography-based radiomic model for the prediction of neoadjuvant immunochemotherapy response in patients with advanced gastric cancer.World J Gastrointest Oncol. 2024 Oct 15;16(10):4115-4128. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v16.i10.4115. World J Gastrointest Oncol. 2024. PMID: 39473942 Free PMC article.
-
Integrating 18F-FDG PET/CT radiomics and body composition for enhanced prognostic assessment in patients with esophageal cancer.BMC Cancer. 2024 Nov 14;24(1):1402. doi: 10.1186/s12885-024-13157-x. BMC Cancer. 2024. PMID: 39543534 Free PMC article.
-
Radiomics and prognostic nutritional index for predicting postoperative survival in esophageal carcinoma.Eur J Med Res. 2025 Mar 17;30(1):178. doi: 10.1186/s40001-025-02358-0. Eur J Med Res. 2025. PMID: 40098023 Free PMC article.
-
Diffusion-Weighted Imaging-Based Radiomics Features and Machine Learning Method to Predict the 90-Day Prognosis in Patients With Acute Ischemic Stroke.Neurologist. 2025 Mar 1;30(2):93-101. doi: 10.1097/NRL.0000000000000599. Neurologist. 2025. PMID: 40035203 Free PMC article.
-
Prediction of Ki-67 expression in bladder cancer based on CT radiomics nomogram.Front Oncol. 2024 Feb 28;14:1276526. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2024.1276526. eCollection 2024. Front Oncol. 2024. PMID: 38482209 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hulshof MCCM, Geijsen ED, Rozema T, Oppedijk V, Buijsen J, Neelis KJ, Nuyttens JJME, van der Sangen MJC, Jeene PM, Reinders JG, et al. Randomized study on dose escalation in definitive chemoradiation for patients with locally Advanced Esophageal Cancer (ARTDECO Study) J Clin Oncology: Official J Am Soc Clin Oncol. 2021;39(25):2816–24. doi: 10.1200/JCO.20.03697. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Verma V, Simone CB, Krishnan S, Lin SH, Yang J, Hahn SM. The Rise of Radiomics and Implications for Oncologic Management.J Natl Cancer Inst2017, 109(7). - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

