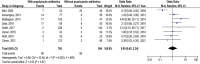The effect of the use of postoperative antibiotic prophylaxis compared with non-use for stented distal hypospadias repair wound: A meta-analysis
- PMID: 37095731
- PMCID: PMC10502256
- DOI: 10.1111/iwj.14182
The effect of the use of postoperative antibiotic prophylaxis compared with non-use for stented distal hypospadias repair wound: A meta-analysis
Retraction in
-
RETRACTION: The Effect of the Use of Postoperative Antibiotic Prophylaxis Compared with Non-Use for Stented Distal Hypospadias Repair Wound: A Meta-Analysis.Int Wound J. 2025 Feb;22(2):e70217. doi: 10.1111/iwj.70217. Int Wound J. 2025. PMID: 39934949 Free PMC article.
Abstract
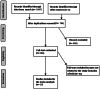
A meta-analysis investigation to measure the influence of the usage of postoperative antibiotic prophylaxis (POP) compared with non-usage for stented distal hypospadias repair (SDHR). A comprehensive literature inspection till February 2023 was applied and 1067 interrelated investigations were reviewed. The 10 chosen investigations enclosed 1398 individuals with SDHR in the chosen investigations starting point, 812 of them were using POP, and 586 were not using POP. Odds ratio (OR) in addition to 95% confidence intervals (CIs) were used to compute the value of the effect of the usage of POP compared with non-usage for SDHR by the dichotomous and continuous approaches and a fixed or random model. No significant difference was found between individuals using POP and not using POP in posthypospadias repair problem (PRP) (OR, 0.99; 95% CI, 0.42-2.34, P = .97) with moderate heterogeneity (I2 = 69%), posthypospadias repair infection problem (PRIP) (OR, 0.56; 95% CI, 0.30-1.06, P = .08) with no heterogeneity (I2 = 15%), and overall composite posthypospadias repair wound healing associated problem (OCPRWHAP) (OR, 1.27; 95% CI, 0.61-2.63, P = .53) with moderate heterogeneity (I2 = 59%) for SDHR. No significant difference was found between individuals using POP and not using POP in PRP, PRIP, and OCPRWHAP for SDHR. However, cautilised of the small sample sizes of several chosen investigations for this meta-analysis, care must be exercised when dealing with its values, for example, the low P-value of the PRIP.
Keywords: posthypospadias repair infection problem; posthypospadias repair problem; postoperative antibiotic prophylaxis; stented distal hypospadias repair.
© 2023 The Authors. International Wound Journal published by Medicalhelplines.com Inc and John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The use of postoperative prophylactic antibiotics in stented distal hypospadias repair: a systematic review and meta-analysis.J Pediatr Urol. 2019 Apr;15(2):138-148. doi: 10.1016/j.jpurol.2018.10.012. Epub 2018 Nov 1. J Pediatr Urol. 2019. PMID: 30527683
-
Non-stented versus stented urethroplasty for distal hypospadias repair: A systematic review and meta-analysis.J Pediatr Urol. 2018 Jun;14(3):212-219. doi: 10.1016/j.jpurol.2017.11.023. Epub 2018 Feb 9. J Pediatr Urol. 2018. PMID: 29580732
-
Analysis of preoperative antibiotic prophylaxis in stented, distal hypospadias repair.Can J Urol. 2017 Apr;24(2):8765-8769. Can J Urol. 2017. PMID: 28436366
-
The usefulness of platelet-rich plasma to manage skin wounds: A meta-analysis.Int Wound J. 2023 Oct;20(8):3123-3130. doi: 10.1111/iwj.14188. Epub 2023 May 1. Int Wound J. 2023. Retraction in: Int Wound J. 2025 Feb;22(2):e70223. doi: 10.1111/iwj.70223. PMID: 37128184 Free PMC article. Retracted.
-
The connotation between perioperative glycemic control approach and sternal wound infection in individuals with diabetes mellitus experiencing cardiac surgery: A meta-analysis.Int Wound J. 2023 Oct;20(8):3324-3330. doi: 10.1111/iwj.14213. Epub 2023 May 15. Int Wound J. 2023. Retraction in: Int Wound J. 2025 Feb;22(2):e70209. doi: 10.1111/iwj.70209. PMID: 37190865 Free PMC article. Retracted.
Cited by
-
RETRACTION: The Effect of the Use of Postoperative Antibiotic Prophylaxis Compared with Non-Use for Stented Distal Hypospadias Repair Wound: A Meta-Analysis.Int Wound J. 2025 Feb;22(2):e70217. doi: 10.1111/iwj.70217. Int Wound J. 2025. PMID: 39934949 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Carmichael SL, Shaw GM, Laurent C, Olney RS, Lammer EJ, Investigation NBDP. Maternal reproductive and demographic characteristics as risk factors for hypospadias. Paediatr Perinat Epidemiol. 2007;21(3):210‐218. - PubMed
-
- Springer A, Tekgul S, Subramaniam R. An update of current practice in hypospadias surgery. Eur Urol Suppl. 2017;16(1):8‐15.
-
- Bhat A. Hypospadiology: Principles and Practices. London: Springer; 2022:295‐313.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials