Exosomes: Nomenclature, Isolation, and Biological Roles in Liver Diseases
- PMID: 37095734
- PMCID: PMC10129856
- DOI: 10.4062/biomolther.2022.161
Exosomes: Nomenclature, Isolation, and Biological Roles in Liver Diseases
Abstract
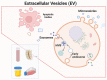
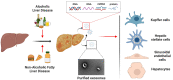
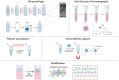
The biogenesis and biological roles of extracellular vesicles (EVs) in the progression of liver diseases have attracted considerable attention in recent years. EVs are membrane-bound nanosized vesicles found in different types of body fluids and contain various bioactive materials, including proteins, lipids, nucleic acids, and mitochondrial DNA. Based on their origin and biogenesis, EVs can be classified as apoptotic bodies, microvesicles, and exosomes. Among these, exosomes are the smallest EVs (30-150 nm in diameter), which play a significant role in cell-to-cell communication and epigenetic regulation. Moreover, exosomal content analysis can reveal the functional state of the parental cell. Therefore, exosomes can be applied to various purposes, including disease diagnosis and treatment, drug delivery, cell-free vaccines, and regenerative medicine. However, exosome-related research faces two major limitations: isolation of exosomes with high yield and purity and distinction of exosomes from other EVs (especially microvesicles). No standardized exosome isolation method has been established to date; however, various exosome isolation strategies have been proposed to investigate their biological roles. Exosome-mediated intercellular communications are known to be involved in alcoholic liver disease and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease development. Damaged hepatocytes or nonparenchymal cells release large numbers of exosomes that promote the progression of inflammation and fibrogenesis through interactions with neighboring cells. Exosomes are expected to provide insight on the progression of liver disease. Here, we review the biogenesis of exosomes, exosome isolation techniques, and biological roles of exosomes in alcoholic liver disease and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease.
Keywords: Biogenesis; Chronic liver disease; Exosome; Extracellular vesicles; Isolation techniques.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Extracellular Vesicles in NAFLD/ALD: From Pathobiology to Therapy.Cells. 2020 Mar 27;9(4):817. doi: 10.3390/cells9040817. Cells. 2020. PMID: 32231001 Free PMC article. Review.
-
[Exosome separation and enrichment technologies and their applications in disease diagnosis and treatment].Se Pu. 2025 May;43(5):434-445. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1123.2024.09007. Se Pu. 2025. PMID: 40331608 Free PMC article. Review. Chinese.
-
Clinical applications of exosome membrane proteins.Precis Clin Med. 2020 Mar;3(1):54-66. doi: 10.1093/pcmedi/pbaa007. Epub 2020 Feb 24. Precis Clin Med. 2020. PMID: 32257533 Free PMC article. Review.
-
[Exosome separation and analysis based on microfluidics technology and its clinical applications].Se Pu. 2025 May;43(5):455-471. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1123.2024.10032. Se Pu. 2025. PMID: 40331610 Free PMC article. Review. Chinese.
-
Urinary extracellular microvesicles: isolation methods and prospects for urinary proteome.Proteomics. 2014 Aug;14(16):1922-32. doi: 10.1002/pmic.201300371. Epub 2014 Jul 28. Proteomics. 2014. PMID: 24962155 Review.
Cited by
-
Exploring extracellular vesicles in zoonotic helminth biology: implications for diagnosis, therapeutic and delivery.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2024 Aug 6;14:1424838. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2024.1424838. eCollection 2024. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 39165921 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Comparison of the efficiency of ultrafiltration, precipitation, and ultracentrifugation methods for exosome isolation.Biochem Biophys Rep. 2024 Feb 21;38:101668. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrep.2024.101668. eCollection 2024 Jul. Biochem Biophys Rep. 2024. PMID: 38405663 Free PMC article.
-
Methods for Extracellular Vesicle Isolation: Relevance for Encapsulated miRNAs in Disease Diagnosis and Treatment.Genes (Basel). 2025 Mar 12;16(3):330. doi: 10.3390/genes16030330. Genes (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40149481 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mesenchymal stem cell exosomes therapy for the treatment of traumatic brain injury: mechanism, progress, challenges and prospects.J Transl Med. 2025 Apr 11;23(1):427. doi: 10.1186/s12967-025-06445-y. J Transl Med. 2025. PMID: 40217480 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Exosomes as a Treatment Option for Osteoarthritis.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Aug 23;25(17):9149. doi: 10.3390/ijms25179149. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39273098 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Avcı E., Balcı-Peynircioğlu B. An overview of exosomes: from biology to emerging roles in immune response. Acta Medica. 2016;47:2–10.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

