The human E3 ligase RNF185 is a regulator of the SARS-CoV-2 envelope protein
- PMID: 37095859
- PMCID: PMC10082641
- DOI: 10.1016/j.isci.2023.106601
The human E3 ligase RNF185 is a regulator of the SARS-CoV-2 envelope protein
Abstract
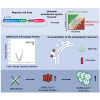
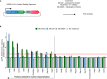
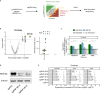
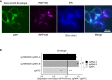
Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) hijacks multiple human proteins during infection and viral replication. To examine whether any viral proteins employ human E3 ubiquitin ligases, we evaluated the stability of SARS-CoV-2 proteins with inhibition of the ubiquitin proteasome pathway. Using genetic screens to dissect the molecular machinery involved in the degradation of candidate viral proteins, we identified human E3 ligase RNF185 as a regulator of protein stability for the SARS-CoV-2 envelope protein. We found that RNF185 and the SARS-CoV-2 envelope co-localize to the endoplasmic reticulum (ER). Finally, we demonstrate that the depletion of RNF185 significantly increases SARS-CoV-2 viral titer in a cellular model. Modulation of this interaction could provide opportunities for novel antiviral therapies.
Keywords: Cell biology; Virology.
© 2023 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
M.S. has received research funding from Calico Life Sciences LLC. B.L.E. has received research funding from Celgene, Deerfield, Novartis, and Calico Life Sciences LLC and consulting fees from GRAIL. He is a member of the scientific advisory board and shareholder for Neomorph Inc., TenSixteen Bio, Skyhawk Therapeutics, and Exo Therapeutics. E.S.F. is a founder, member of the scientific advisory board (SAB), and equity holder of Civetta Therapeutics, Proximity Therapeutics, and Neomorph Inc (also board of directors), a SAB member and equity holder in Avilar Therapeutics and Photys Therapeutics, equity holder in Lighthorse Therapeutics, and a consultant to Sanofi, Novartis, Deerfield, Odyssey Therapeutics, and EcoR1 capital. The Fischer laboratory receives or has received research funding from Novartis, Deerfield, Ajax, Interline, and Astellas. K.A.D. is a consultant to Kronos Bio and Neomorph Inc. A.S.S. reports consulting fees from Adaptive Technologies and Roche.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Human E3 ubiquitin ligases: accelerators and brakes for SARS-CoV-2 infection.Biochem Soc Trans. 2024 Oct 30;52(5):2009-2021. doi: 10.1042/BST20230324. Biochem Soc Trans. 2024. PMID: 39222407 Free PMC article. Review.
-
RNF185 is a novel E3 ligase of endoplasmic reticulum-associated degradation (ERAD) that targets cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator (CFTR).J Biol Chem. 2013 Oct 25;288(43):31177-91. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M113.470500. Epub 2013 Sep 9. J Biol Chem. 2013. PMID: 24019521 Free PMC article.
-
UBR5 Acts as an Antiviral Host Factor against MERS-CoV via Promoting Ubiquitination and Degradation of ORF4b.J Virol. 2022 Sep 14;96(17):e0074122. doi: 10.1128/jvi.00741-22. Epub 2022 Aug 18. J Virol. 2022. PMID: 35980206 Free PMC article.
-
The E3 Ubiquitin Ligase RNF5 Facilitates SARS-CoV-2 Membrane Protein-Mediated Virion Release.mBio. 2021 Feb 22;13(1):e0316821. doi: 10.1128/mbio.03168-21. Epub 2022 Feb 1. mBio. 2021. PMID: 35100873 Free PMC article.
-
Spatial and temporal roles of SARS-CoV PLpro -A snapshot.FASEB J. 2021 Jan;35(1):e21197. doi: 10.1096/fj.202002271. FASEB J. 2021. PMID: 33368679 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Lung-Targeted Lipid Nanoparticle-Delivered siUSP33 Attenuates SARS-CoV-2 Replication and Virulence by Promoting Envelope Degradation.Adv Sci (Weinh). 2024 Nov;11(42):e2406211. doi: 10.1002/advs.202406211. Epub 2024 Sep 20. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2024. PMID: 39301916 Free PMC article.
-
Human E3 ubiquitin ligases: accelerators and brakes for SARS-CoV-2 infection.Biochem Soc Trans. 2024 Oct 30;52(5):2009-2021. doi: 10.1042/BST20230324. Biochem Soc Trans. 2024. PMID: 39222407 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mechanisms of substrate processing during ER-associated protein degradation.Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2023 Nov;24(11):777-796. doi: 10.1038/s41580-023-00633-8. Epub 2023 Aug 1. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2023. PMID: 37528230 Review.
-
Targeted protein degradation: from mechanisms to clinic.Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2024 Sep;25(9):740-757. doi: 10.1038/s41580-024-00729-9. Epub 2024 Apr 29. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2024. PMID: 38684868 Review.
-
Niclosamide: CRL4AMBRA1 mediated degradation of cyclin D1 following mitochondrial membrane depolarization.RSC Med Chem. 2025 May 6;16(7):3049-3057. doi: 10.1039/d5md00054h. eCollection 2025 Jul 16. RSC Med Chem. 2025. PMID: 40337304 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Sheahan T.P., Sims A.C., Zhou S., Graham R.L., Pruijssers A.J., Agostini M.L., Leist S.R., Schäfer A., Dinnon K.H., 3rd, Stevens L.J., et al. An orally bioavailable broad-spectrum antiviral inhibits SARS-CoV-2 in human airway epithelial cell cultures and multiple coronaviruses in mice. Sci. Transl. Med. 2020;12:eabb5883. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Owen D.R., Allerton C.M.N., Anderson A.S., Aschenbrenner L., Avery M., Berritt S., Boras B., Cardin R.D., Carlo A., Coffman K.J., et al. An oral SARS-CoV-2 M(pro) inhibitor clinical candidate for the treatment of COVID-19. Science. 2021;374:1586–1593. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

