Short- and long term antibacterial effects of a single rinse with different mouthwashes: A randomized clinical trial
- PMID: 37095907
- PMCID: PMC10121446
- DOI: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e15350
Short- and long term antibacterial effects of a single rinse with different mouthwashes: A randomized clinical trial
Retraction in
-
Retraction notice to "Short- and long term antibacterial effects of a single rinse with different mouthwashes: A randomized clinical trial" [Heliyon 9 (2023) e15350].Heliyon. 2025 Mar 12;11(6):e43145. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2025.e43145. eCollection 2025 Mar 20. Heliyon. 2025. PMID: 40201511 Free PMC article.
Abstract
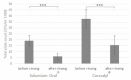
Objectives: Reducing the microbial level in the aerosol created during dental procedures is essential to avoiding infections. The aim of this study was to examine the change in Streptococcus mutans (S. mutans) and the total bacterial load in human saliva in vivo after a single rinse with different mouthwashes.
Material and methods: One mL of unstimulated saliva was collected from volunteers with poor oral hygiene at baseline and 5 min after a 1-min rinsing with diluted Solumium Oral® (hyper-pure 0.0015% chlorine dioxide; ClO2), Listerine Total Care®, Corsodyl® (0.2% chlorhexidine-digluconate; CHX), or BioGate Si*CLEAN for bacterial investigation. In a second study, volunteers rinsed with 0.003% ClO2 or CHX for 1 min, and saliva was collected at baseline, after 5 min, and after 90 min. After plating, the total plate and S. mutans colony numbers were determined.
Results: In the first study, ClO2 and CHX similarly reduced both total germ and S. mutans numbers, while Listerine Total Care® decreased only the S. mutans counts. BioGate Si*Clean had no effect on either the total germ or S. mutans numbers. In the second study, an increasing tendency toward bacterial regrowth was observed with CHX after 90 min compared to the 5-min value, while no change was measured after ClO2 rinsing.
Conclusion: Hyper-pure ClO2 rinsing may be a new promising preventive and therapeutic adjuvant in dental practice, as it is similar in effectiveness to the gold standard CHX-containing mouthwashes, especially in patients concerned with taste or tooth discoloration during oral health therapy.
Keywords: Chlorhexidine; Hyper-pure chlorine dioxide; Listerine; Mouthwash; Salivary bacteria; Single rinse; Streptococcus mutans.
© 2023 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Károlyházy K., Fazekas B., Fazekas J., Hermann P., Marton K. Ebola virus disease: awareness among dental students in Hungary. Acta Microbiol. Immunol. Hung. 2016;63(3):325–337. - PubMed
-
- Kály-Kullai K., Wittmann M., Nosztriczius Z., Rosivall L. Can Clorine dioxide prevent the spreading of coronavirus or other viral infections? Phys. Int. 2020;107(1):1–11. - PubMed
-
- Balejo Rodrigo Dalla Pria, Cortelli J.R., Costa Fernando Oliveira, Cyrino Renata Magalhães, Aquino Davi Romeiro, Cogo-Müller Karina, Miranda Taís Browne, Moura Sara Porto, Cortelli Sheila Cavalca. Effects of chlorhexidine preprocedural rinse on bacteremia in periodontal patients: a randomized clinical trial. J. Appl. Oral Sci. 2017;25:586–595. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

